Untapped potential of stem cells could aid repair of spinal cord damage
Caption
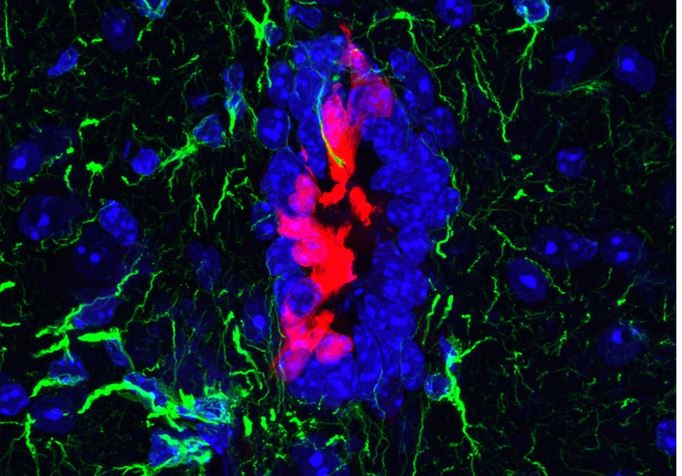
Image of uninjured mice spinal cord, with ependymal cells shown in red.
Credit: Bruno Frederico
Scientists at the Francis Crick Institute have identified a group of latent stem cells that respond to injury in the central nervous system of mice. If a similar type of cell exists in humans, they could offer a new therapeutic approach to treat brain and spinal cord injuries.
After disease or injury, stem cells help repair the damage by replacing cells that have died. In some organs, like the skin and intestine, these stem cells are constantly active, while in others, so called ‘latent stem cells’ lie waiting for harm to occur before being triggered into action.
In their study published in Developmental Cell today (Monday 22 August), the researchers identified a group of latent stem cells in the central nervous system of mice. These are part of the ependymal cells that line the walls of compartments in the brain and spinal cord that hold cerebrospinal fluid.
The cells were identified by chance when the team used a fluorescence tool to look for immune cells called dendritic cells in the brain. The ependymal cells that the tool identified were found to arise from embryonic progenitor cells that shared a same protein as dendritic cells on their surface, which revealed them to the scientists.
Working with neuroscientist colleagues at the Francis Crick Institute and developmental biologists at the Institute of Molecular Medicine in Lisbon, they found that in healthy mice, these cells stay still and waft small hairs on their surface to help the flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
However, in injured mouse spinal cords, these cells responded by dividing, migrating towards the damaged area and differentiating into astrocytes, one of the major cell types of the nervous system.
The team also looked at these cells in detail in the lab and found they demonstrated key hallmarks of stem cell behaviour. They divided continuously over a long period of time, and were also able to differentiate into all three main cell types of the central nervous system – neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes.
Bruno Frederico, co-corresponding author and postdoctoral training fellow in the Immunobiology laboratory at the Crick says, “While we don’t know if these cells exist in humans, if they do, it would be interesting to see if they also default to becoming astrocytes rather than neurons in response to damage. This might help explain why the mammalian central nervous system does not have a strong ability to repair itself after injury.
“If we could find a way to overcome the barriers that are stopping the differentiation into neurons and oligodendrocytes after spinal cord injury, it could present a new avenue of therapies to treat spinal cord injuries.”
The researchers suggest that unlocking the potential of these cells could help the body produce new neurons, which are responsible for receiving and sending key signals for movement, after spinal injury.
Caetano Reis e Sousa, co-corresponding author and principal group leader at the Crick, says: “There was uncertainty over whether ependymal cells can have neural stem cell capabilities, but this study underscores their potential.
“We hope that studying these cells will help build a more complete picture of the role different types of stem cells play in repairing damage, which could have important implications for regenerative medicine.”
For further information, contact: press@crick.ac.uk or +44 (0)20 3796 5252
Notes to Editors
Reference: Frederico, B. et al. (2022). DNGR-1-tracing marks an ependymal cell subset with damage-responsive neural stem cell potential. Developmental Cell. 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.07.012
The Francis Crick Institute is a biomedical discovery institute dedicated to understanding the fundamental biology underlying health and disease. Its work is helping to understand why disease develops and to translate discoveries into new ways to prevent, diagnose and treat illnesses such as cancer, heart disease, stroke, infections, and neurodegenerative diseases.
An independent organisation, its founding partners are the Medical Research Council (MRC), Cancer Research UK, Wellcome, UCL (University College London), Imperial College London and King’s College London.
The Crick was formed in 2015, and in 2016 it moved into a brand new state-of-the-art building in central London which brings together 1500 scientists and support staff working collaboratively across disciplines, making it the biggest biomedical research facility under a single roof in Europe.
Journal: Developmental Cell
DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.07.012
Method of Research: Experimental study
Subject of Research: Animals
Article Title: DNGR-1-tracing marks an ependymal cell subset with damage-responsive neural stem cell potential
Article Publication Date: 22-Aug-2022
Media Contact
Alice Deeley
The Francis Crick Institute
alice.deeley@crick.ac.uk
Office: 020-379-6536
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Making diamonds at ambient pressure
Scientists develop novel liquid metal alloy system to synthesize diamond under moderate conditions. Did you know that 99% of synthetic diamonds are currently produced using high-pressure and high-temperature (HPHT) methods?[2]…

Eruption of mega-magnetic star lights up nearby galaxy
Thanks to ESA satellites, an international team including UNIGE researchers has detected a giant eruption coming from a magnetar, an extremely magnetic neutron star. While ESA’s satellite INTEGRAL was observing…

Solving the riddle of the sphingolipids in coronary artery disease
Weill Cornell Medicine investigators have uncovered a way to unleash in blood vessels the protective effects of a type of fat-related molecule known as a sphingolipid, suggesting a promising new…





















