Toward a Better Drug against Malaria
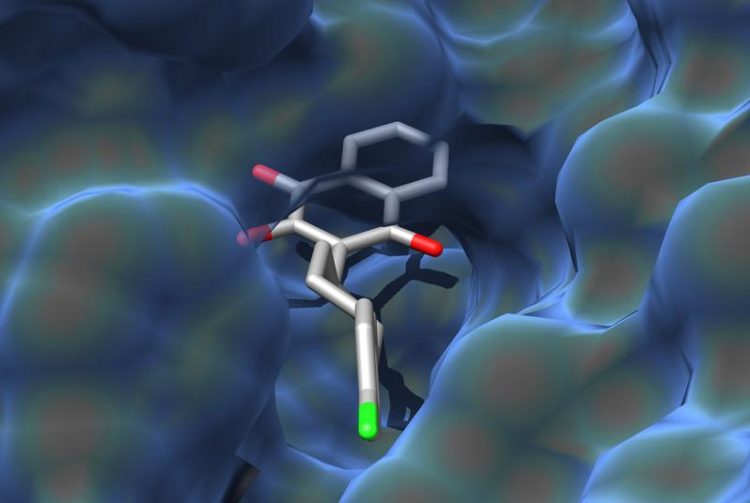
Molecule in a pocket: The illustration shows how atovaquone binds to its target protein. Graphic: Dominic Birth, Carola Hunte
A research team led by Prof. Dr. Carola Hunte has succeeded in describing how the antimalarial drug atovaquone binds to its target protein. The scientists used x-ray crystallography to determine the three-dimensional structure of the protein with the active substance bound.
The drug combination atovaquone-proguanil (Malarone®) is a medication used worldwide for the prevention and treatment of malaria. The data and the resulting findings concerning the mode of action of atovaquone could lead to improved medications against the tropical disease.
Hunte and her team conducted the research at the Institute for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of the Faculty of Medicine and the Centre for Biological Signalling Studies BIOSS at the University of Freiburg. The scientists published their findings in the journal Nature Communications.
Malaria is one of the most dangerous tropical diseases in the world. Anopheles mosquitoes infected with Plasmodium species – unicellular parasites – transmit the disease by biting. Atovaquone blocks a protein of the respiratory chain in the mitochondria, the power plants of the cell, thus killing off the parasites.
However, the pathogen is susceptible to mutations so that drug resistant strains are arising and spreading. The Freiburg scientists have now paved the way for the development of improved drugs by revealing the precise binding mode of atovaquone to the target protein.
They used the mitochondrial protein from cells of baker’s yeast for their analyses due to its close resemblance to the parasitic protein.
The target protein of atovaquone is the third of four enzymes of the respiratory chain in the mitochondrion. The amino acid chains of the protein form a three-dimensional pocket. The molecule of the active substance fits perfectly into this pocket, binding to amino acids at numerous positions.
These interactions are crucial for the effect atovaquone has in Plasmodium cells, ultimately leading to the death of the pathogen. The researchers conducted a protein sequence analysis, revealing that most of these docking sites are identical in the pathogen, baker’s yeast and in human cells. Atovaquone forms several bonds that are specific to the Plasmodium protein in the open area of the binding pocket.
In addition, the structural analysis revealed the molecular basis of resistances: Due to mutations that change the structure of the target protein, the substance cannot reach the designated binding mode – it doesn’t fit perfectly into the pocket anymore.
The data provides an important basis for improving antimalarial drugs. Scientists could now modify the molecular structure of atovaquone by means of structure-based drug design, ensuring that the active substance forms necessary bonds – and that the pathogen is no longer resistant to it.
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Carola Hunte
Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology / BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies
University of Freiburg
Phone: +49 (0)761/203-5279
E-Mail: carola.hunte@biochemie.uni-freiburg.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















