Researchers discover a new embryonic brain circuit
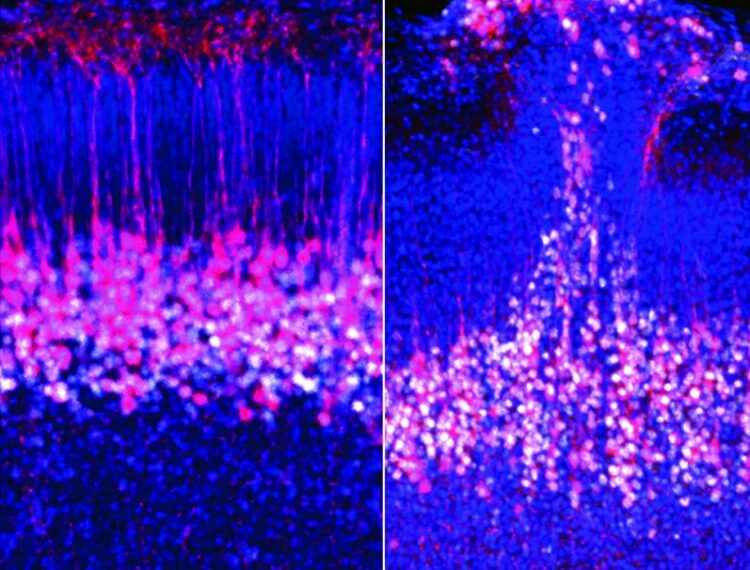
Layer 5 pyramidal neurons in normal mice (left) compared with mice with autism gene knocked-out (right), showing a patch of disorganized cortex.
Credit: Institute of Molecular and Clinical Ophthalmology Basel (IOB)
The findings may provide new insights into circuit abnormalities in autism.
Using a new approach for studying live embryonic mouse brains at single-cell resolution, researchers have identified an active multi-layer circuit that forms in the cortex during an unexpectedly early stage of development. Perturbing the circuit genetically led to changes similar to those seen in the brains of people with autism. The findings are reported today in Cell by a team based at the Institute of Molecular and Clinical Ophthalmology Basel.
“Understanding the detailed development of cell types and circuits in the cortex can provide important insights into autism and other neurodevelopmental diseases,” says Botond Roska, Director at IOB and the paper’s corresponding author. “This is what our findings confirm.”
Autism has long been associated with faulty circuits in the cortex, which is the part of the brain that governs sensory perception, cognition, and other high-order functions. Most of the cortex is composed of excitatory cells called pyramidal neurons. The IOB team wanted to study when and how these neurons assemble into the first active circuits in the cortex, but that posed a difficult challenge. Pyramidal neurons measure only a tenth of the width of a human hair, and any movement during experimental procedures might lead to inaccurate recordings of activity. To keep the neurons stable for research, the team devised a surgical solution: Embryos were secured inside of agar-filled 3D holding devices within the mother’s abdominal cavity, so that normal embryonic blood flow and temperature could be maintained.
The prevailing view is that the cortex develops in an “inside out fashion”, with the deepest of its six layers appearing first. Seen this way, pyramidal neurons were thought to slowly become active as they migrate to their final locations in the cortex and form connections with each other. But during the research, “we actually detected a very different activity pattern,” says Arjun Bharioke, a systems neuroscientist in IOB’s Central Visual Circuits Group, and one of the paper’s two lead authors. Focusing specifically on pyramidal neurons that develop into layer 5 of the cortex, the team discovered a very early transient circuit that was already highly active and correlated even before the six-layer cortex had formed. This indicates that the neurons were already connected prior to their migration to form layer 5. The transient circuit initially had 2 layers: a deep layer and a superficial layer. Later, the superficial layer became silent and vanished, while the classical layer-by-layer cortical development resumed, with a third intermediate layer forming layer 5.
“We also wanted to understand how this circuit changes in an autism model,” says Martin Munz, an IOB developmental biologist in the Central Visual Circuits Group and the paper’s other lead author. Working with knock-out mouse lines missing one or both alleles of two autism-associated genes–Chd8 and Grin2b–the team made a key finding. The absence of these genes is known to cause significant autism in children. And in homozygous and heterozygous knockout mice, the superficial layer remained active as a developmental remnant. “Throughout embryonic development, it never disappeared,” Munz says. Moreover, the knockout mouse brains contained patchy areas of cortical disorganization similar to those seen in people with autism.
The findings suggest that the spatial organization of pyramidal neurons is regulated by the newly-found circuit, and that “changes to embryonic circuits play a role in dysfunctions associated with neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism spectrum disorder,” Bharioke says.
In future research, IOB researchers will “carefully look at the superficial and deep layers of this early circuitry and independently manipulate them,” Roska says. “This will be instructive for learning about the etiology of neurodevelopmental diseases.”
Original Publication:
Pyramidal neurons form active, transient, multilayered circuits perturbed by autism-associated mutations at the inception of neocortex
Martin Munz, Arjun Bharioke, Georg Kosche, Verónica Moreno-Juan, Alexandra Brignall, Tiago M. Rodrigues, Alexandra Graff-Meyer, Talia Ulmer, Stephanie Haeuselmann, Dinko Pavlinic, Nicole Ledergeber, Brigitte Gross-Scherf, Balázs Rózsa, Jacek Krol, Simone Picelli, Cameron S. Cowan, Botond Roska
2023, Cell 186
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2023.03.025
About IOB
At the Institute of Molecular and Clinical Ophthalmology Basel (IOB), basic researchers and clinicians work hand in hand to advance the understanding of vision and its diseases, and to develop new therapies for vision loss. IOB started its operations in 2018. The institute is constituted as a foundation, granting academic freedom to its scientists. Founding partners are the University Hospital Basel, the University of Basel and Novartis. The Canton of Basel-Stadt has granted the institute substantial financial support.
www.iob.ch
Follow us on Social Media
Twitter @IOB_ch
YouTube IOB Basel Switzerland
IOB Media Contact:
clara.vuille-dit-bille@iob.ch
Journal: Cell
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.03.025
Method of Research: Experimental study
Subject of Research: Animals
Article Title: Pyramidal neurons form active, transient, multilayered circuits perturbed by autism-associated mutations at the inception of neocortex
Article Publication Date: 17-Apr-2023
Media Contact
Clara Vuille-dit-Bille
Institute of Molecular and Clinical Ophthalmology Basel
clara.vuille-dit-bille@iob.ch
Original Source
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…





















