How our ancestors were like gorillas – fossils illustrate sex differences in growth and the costs of being a male

“It’s common knowledge that boys mature later than girls, but in humans the difference is actually much less marked than in some other primates. Male gorillas continue to grow long after their wisdom teeth have come through, and they don't reach what is referred to as dominant “silverback” status until many years after the females have already started to have offspring. Our research makes us think that, in this fossil species, one older male was probably dominant in a troop of females. This situation was risky for the males and they suffered high rates of predation as a result of both their social structure and pattern of growth.”
The research used 35 fossilised specimens of Paranthropus robustus, an extinct relative of Homo sapiens which existed almost two million years ago. The fossils came from the palaeontological sites of Swartkrans, Drimolen and Kromdraii, all of which are in South Africa’s Cradle of Humankind World Heritage Site near Johannesburg.
The research was inspired by earlier discoveries at Drimolen by Dr Andre Keyser, one of the co-authors of the study. Dr Colin Menter, from the University of Johannesburg and co-director of current fieldwork at Drimolen, explains: “Discoveries at this site showed us that sex differences in Paranthropus robustus were greater than we had previously thought. While there are some specimens from Drimolen that are just as large and robust as those from other sites like Swartkrans, there is a complete female skull that is distinctly smaller than the other, well-preserved specimens of the species.”
Jacopo Moggi-Cecchi, based at the University of Florence and an expert on fossil teeth, participated in the study and says: “It takes large samples of fossils to ask questions about variation and growth, and it's really a tribute to fieldworkers such as Robert Broom and Bob Brain [who worked at Swartkrans] that this research could even take place. It's also an example of why we need to continue to look for fossils after we think we know what a species is – more specimens allow us to answer more interesting questions. Even isolated teeth can give us new insights into what variation means.”
Dr Lockwood adds: “The pattern of growth also gives a better understanding of who is male and who is female in this sample of skulls and it turns out that there are far more males in the fossil sample. Because fossils from the most prolific site, Swartkrans, are thought to have been deposited by predators such as leopards and hyenas, it appears that males were getting killed more often than females.
“Basically, males had a high-risk, high-return lifestyle in this species. They most likely left their birth groups at about the time they reached maturity, and it was a long time before they were mature enough to attract females and establish a new group. Some of them were killed by predators before they got the chance.”
A final point made by the researchers is that not all fossil hominin samples show the same patterns, and it is quite possible that further work will reveal clear diversity in social structure between human ancestors, in the same way that one sees differences among apes such as chimpanzees, bonobos, gorillas, and orangutans. This research will help us to understand how human social structure evolved.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.ucl.ac.ukAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…
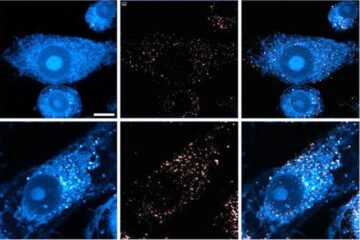
Innovative microscopy demystifies metabolism of Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Diego have deployed state-of-the art imaging techniques to discover the metabolism driving Alzheimer’s disease; results suggest new treatment strategies. Alzheimer’s disease causes significant problems with memory,…
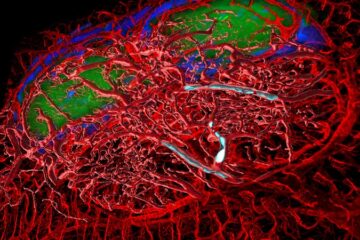
A cause of immunodeficiency identified
After stroke and heart attack: Every year, between 250,000 and 300,000 people in Germany suffer from a stroke or heart attack. These patients suffer immune disturbances and are very frequently…





















