Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

Embryonic pig cell transplants halt rat diabetes
Procedure requires no immune suppression drugs
An experimental cross-species transplant to treat diabetes has passed an early test in rats with better-than-expected results, suggesting the innovative approach might halt type 1 diabetes while greatly reducing the risk of rejection.
Scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis set up control and experimental groups of rats with diabetes. The experimental group received embryonic pig pancreas cell transpl

Marsupial among model organisms next in line for sequencing
NHGRI-supported centers also to target more insects, worms and fungi
The Large-Scale Sequencing Research Network this year will begin sequencing the genomes of more than a dozen new model organisms, including the first marsupial to have its DNA deciphered. The research network, supported by the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), one of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), is part of an effort to further advance understanding of the human genome.
The effort

Researchers discover new family of Atlantic corals, upset prior coral classifications
Provides new look at conservation of threatened coral species
An international research team has identified a family of corals found only in the Atlantic Ocean-a first for such classifications in that ocean-in a study that could transform how corals are viewed and classified. The scientists, who will publish their results in the Feb. 26 issue of the journal Nature, say the findings are also important for future decisions about coral conservation and the preservation of threatened biod
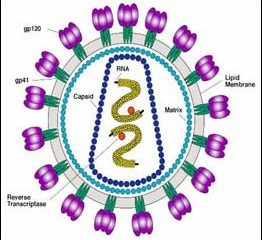
Scientists find HIV-blocking protein in monkeys
Scientists at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have identified a protein that blocks HIV replication in monkey cells. Humans have a similar protein, although it is not as effective at stopping HIV, say the researchers whose work is published in this week’s issue of Nature. The team, headed by Joseph Sodroski, M.D., is supported by the NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
“Identification of this HIV-blocking factor opens new avenues for intervening in the ear

Stress gene found in plants
A single gene has been discovered that helps plants cope with stressful situations such as disease or poor environments – according to a report published in Nature, 26 February 2004.
Scientists at the universities of Bristol and Oxford isolated and characterised the gene called OXI1 from thale cress, a common roadside weed. OXI1 boosts the plant’s ability to stop fungal infection from spreading, and helps roots to grow despite poor conditions.
Dr Claire Grierson from Bristol

Researchers map ’super-tree’ of flowering plants, solving Darwin’s "abominable mystery"
The secret of how flowering plants evolved into one of the Earth’s most dominant and diverse groups of organisms is revealed in study led by researchers from the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Imperial College London.
Described by Charles Darwin as an “abominable mystery”, the team publish the first complete evolutionary ’super-tree’ of relationships among all families of flowering plants in current edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science.
Using a combination