New platform based on biology and nanotechnology carries mRNA directly to target cells
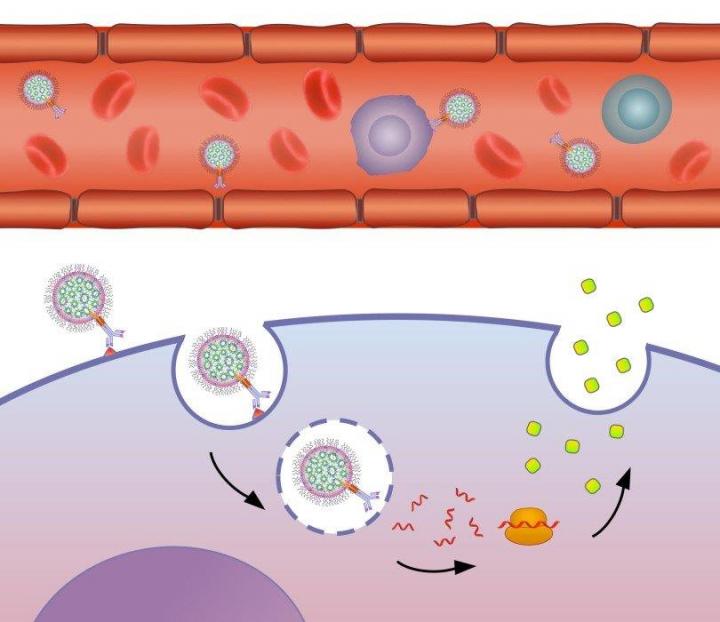
Schematic illustration of the mechanism by which the lab's targeted nanoparticles modulate gene expression in the target cell. Credit: Nuphar Veiga/American Friends of Tel Aviv University
Delivering an effective therapeutic payload to specific target cells with few adverse effects is considered by many to be the holy grail of medical research. A new Tel Aviv University study explores a biological approach to directing nanocarriers loaded with protein “game changers” to specific cells. The groundbreaking method may prove useful in treating myriad malignancies, inflammatory diseases and rare genetic disorders.
Prof. Dan Peer, director of the Laboratory of Precision Nanomedicine at the School of Molecular Cell Biology at TAU's Faculty of Life Sciences, led the research for the new study, which was conducted by TAU graduate student Nuphar Veiga and lab colleagues Meir Goldsmith, Yasmin Granot, Daniel Rosenblum, Niels Dammes, Ranit Kedmi and Srinivas Ramishetti. The research was published in Nature Communications.
Over the past few years, lipid carriers encapsulating messenger RNAs (mRNAs) have been shown to be extremely useful in altering the protein expressions for a host of diseases. But directing this information to specific cells has remained a major challenge.
“In our new research, we utilized mRNA-loaded carriers — nanovehicles carrying a set of genetic instructions via a biological platform called ASSET — to target the genetic instructions of an anti-inflammatory protein in immune cells,” says Prof. Peer. “We were able to demonstrate that selective anti-inflammatory protein in the target cells resulted in reduced symptoms and disease severity in colitis.
“This research is revolutionary. It paves the way for the introduction of an mRNA that could encode any protein lacking in cells, with direct applications for genetic, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases — not to mention cancer, in which certain genes overexpress themselves.”
ASSET (Anchored Secondary scFv Enabling Targeting) uses a biological approach to direct nanocarriers into specific cells to promote gene manipulation.
“This study opens new avenues in cell-specific delivery of mRNA molecules and ultimately might introduce the specific anti-inflammatory (interleukin 10) mRNA as a novel therapeutic modality for inflammatory bowel diseases,” says Ms. Veiga.
“Targeted mRNA-based protein production has both therapeutic and research applications,” she concludes. “Going forward, we intend to utilize targeted mRNA delivery for the investigation of novel therapeutics treating inflammation disorders, cancer and rare genetic diseases.”
###
American Friends of Tel Aviv University supports Israel's most influential, comprehensive and sought-after center of higher learning, Tel Aviv University (TAU). TAU is recognized and celebrated internationally for creating an innovative, entrepreneurial culture on campus that generates inventions, startups and economic development in Israel. TAU is ranked ninth in the world, and first in Israel, for producing start-up founders of billion-dollar companies, an achievement that surpassed several Ivy League universities. To date, 2,500 US patents have been filed by Tel Aviv University researchers — ranking TAU #1 in Israel, #10 outside of the US and #43 in the world.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Octopus inspires new suction mechanism for robots
A new robotic suction cup which can grasp rough, curved and heavy stone, has been developed by scientists at the University of Bristol. The team, based at Bristol Robotics Laboratory,…

Peptides on Interstellar Ice
A research team led by Dr Serge Krasnokutski from the Astrophysics Laboratory at the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy at the University of Jena had already demonstrated that simple peptides…

A new look at the consequences of light pollution
GAME 2024 begins its experiments in eight countries. Can artificial light at night harm marine algae and impair their important functions for coastal ecosystems? This year’s project of the training…





















