New Insights into Evolution
Complex evolutionary relationships: Long-term expression in one organ predisposes genes for later use in other organs.
Kenji Fukushima / University of Würzburg
The long-term expression of genes in vertebrate organs predisposes these genes to be subsequently utilized in other organs during evolution. The scientists Kenji Fukushima and David D. Pollock report this finding in the journal Nature Communications.
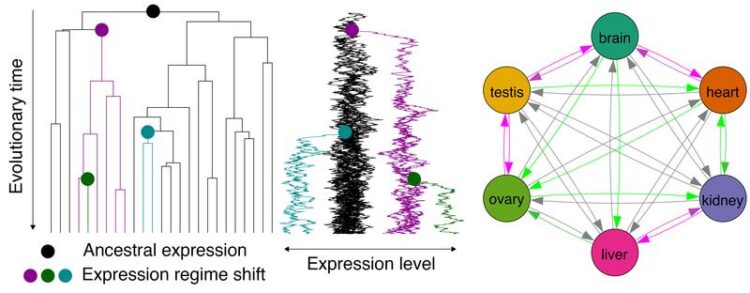
Vertebrate organs organize physiological activities, and the diverse expression patterns of thousands of genes determines organ identities and functions. Because of this, the evolution of gene expression patterns plays a central role in organismal evolution.
Major organ-altering evolutionary events such as development of the hominoid brain are also associated with gene expression shifts. However, although gene duplication is well-known to play an important role in expression pattern shifts, the evolutionary dynamics of expression patterns with and without gene duplication remain poorly understood.
„An important question is whether long-term expression in one organ predisposes genes to be subsequently utilized in other organs. The answer is yes“, says Dr. Kenji Fukushima from Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany. „There are preadaptive propensities in the evolution of vertebrate gene expression, and the propensity varies with the presence and type of gene duplication.“
Funded by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation
Kenji Fukushima now reports this and other findings with his co-author David D. Pollock (University of Colorado, School of Medicine, Aurora, USA) in the journal Nature Communications.
Dr. Fukushima holds a research position at the JMU Chair for Molecular Plant Physiology and Biophysics. Here, since 2018, the Japanese evolution biologist has been building up a working group, funded with 1.6 million euros by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. The renowned foundation had selected him as the winner of its Sofja Kovalevskaja Prize 2018. The award is intended for exceptionally talented young researchers.
Complex history of gene family trees
For their study the scientists amalgamated 1,903 RNA-seq datasets from 182 research projects. The date include six organs (brain, heart, kidney, liver, ovary, and testis) from 21 vertebrate species, ranging from freshwater fish and frogs to lizards, birds, rodents and humans. So they revealed a complex history of gene family trees. This allowed them to analyse the evolutionary expression of a broad set of genes.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Dr. Kenji Fukushima, University of Würzburg, kenji.fukushima@uni-wuerzburg.de
Originalpublikation:
Amalgamated cross-species transcriptomes reveal organ-specific propensity in gene expression evolution, Kenji Fukushima & David D. Pollock, Nature Communications, Open Access, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18090-8
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















