Natural Killer Cells Coordinate Wound Healing
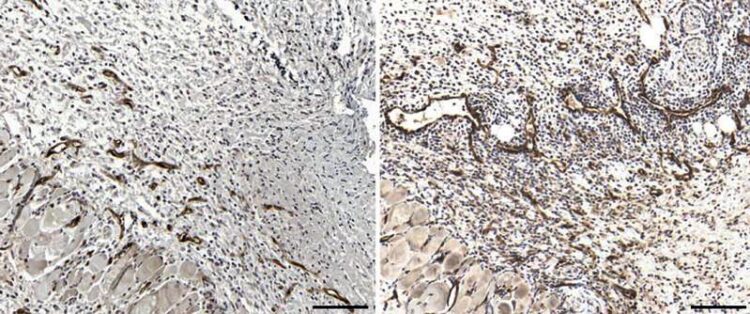
Immunohistochemical imaging of blood vessels in skin lesions during bacterial infection in a mouse without the signaling factor (right) and a normal mouse (left)
(c) UZH
Natural killer cells do not just kill cancer cells or cells infected with viruses, they also mediate a trade-off between wound healing and bacterial defense in skin wounds. If the healing process is accelerated, the immune defense is weakened, researchers at the University of Zurich have now shown. This has relevance in treating skin injuries and in tackling antibiotic-resistant germs.
Natural killer cells are a specific type of immune cell. They recognize abnormal body cells such as cancer cells or virus-infected cells, and eliminate them. An international research team led by Christian Stockmann, professor at the Institute of Anatomy at the University of Zurich (UZH), has now discovered that killer cells have another – surprising – function: They manage wound healing in the skin. “We were able to genetically modify these cells in mice to accelerate the growth of blood vessels and cause skin wounds to close more quickly. However, this has the effect of weakening the immune defense, thereby increasing susceptibility to bacterial infections,” says Stockmann.
Accelerated wound healing carries higher risk of infection
Biomedical research has focused heavily on finding ways of influencing wound-healing processes. Above all, researchers have sought methods to stimulate and accelerate the formation of new blood vessels – either directly or indirectly by influencing the immune response. However, Stockmann advises caution here: “Our results show that there may be an increased risk of infection associated with such approaches.”
Another open question is the extent to which natural killer cells influence not only the speed but also the quality of wound healing – for example, the composition of connective tissue or the regeneration of hair follicles, glands and other skin components. “The most interesting question is how we can manage to accelerate wound healing while also strengthening the immune defense against infections,” says Stockmann.
Harnessing killer cells to fight antibiotic-resistant bacteria
The immunologist and anatomist also sees further potential in killer cells. Modern cancer treatments already use therapeutic agents that activate and stimulate killer cells so that they kill the cancer cells more aggressively. “Our data suggest that these types of agents may also be effective against bacterial infections – something that should definitely be explored further in light of the increasing number of antibiotic-resistant bugs,” Stockmann says.
Natural killer cells communicate continuously with other defense cells and influence their activity. To do this, they secrete messenger substances known as cytokines. In their study, the researchers realized that killer cells also infiltrate skin injuries with very low levels of oxygen (hypoxia). In such tissues, killer cells change their gene expression to adapt to the lack of oxygen. Hypoxia-inducible transcription factors (HIF) are responsible for this adaptation. In mice, if one of these factors called HIF-1α is missing, the release of certain cytokines is impaired. In response, blood vessels grow more quickly in the skin, thus accelerating wound healing. At the same time, however, the fight against bacterial infections is restricted. The balance then tips in favor of wound healing, but with a higher risk of infection.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Prof. Dr. Christian Stockmann
Institute of Anatomy
University of Zurich
Phone: +41 44 635 53 00
E-mail: christian.stockmann@anatomy.uzh.ch
Originalpublikation:
Michal Sobecki, Ewelina Krzywinska, Shunmugam Nagarajan, et. al. NK cells in hypoxic skin mediate a trade-off between wound healing and antibacterial defence. Nature Communications. 4 August 2021. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25065-w
Weitere Informationen:
https://www.media.uzh.ch/en/Press-Releases/2021/Wound-Healing.html
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

“Nanostitches” enable lighter and tougher composite materials
In research that may lead to next-generation airplanes and spacecraft, MIT engineers used carbon nanotubes to prevent cracking in multilayered composites. To save on fuel and reduce aircraft emissions, engineers…

Trash to treasure
Researchers turn metal waste into catalyst for hydrogen. Scientists have found a way to transform metal waste into a highly efficient catalyst to make hydrogen from water, a discovery that…

Real-time detection of infectious disease viruses
… by searching for molecular fingerprinting. A research team consisting of Professor Kyoung-Duck Park and Taeyoung Moon and Huitae Joo, PhD candidates, from the Department of Physics at Pohang University…





















