Nanotubes built from protein crystals: Breakthrough in biomolecular engineering
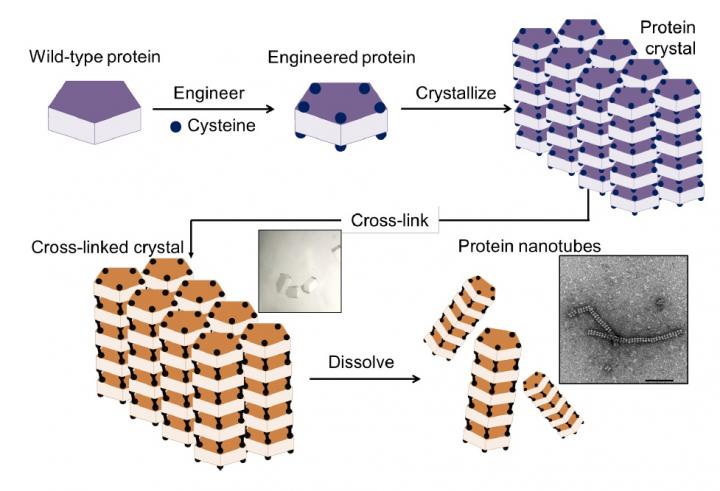
The method involved a four-step process: 1) introduction of cysteine residues into the wild-type protein; 2) crystallization of the engineered protein into a lattice structure; 3) formation of a cross-linked crystal; and 4) dissolution of the scaffold to release the protein nanotubes. Credit: Chemical Science
An innovative way for assembly of proteins into well-ordered nanotubes has been developed by a group led by Takafumi Ueno at Tokyo Tech's Department of Biomolecular Engineering.
Tailor-made protein nanostructures are of intense research interest, as they could be used to develop highly specific and powerful catalysts, targeted drug and vaccine delivery systems, and for the design of many other promising biomaterials.
Scientists have faced challenges in constructing protein assemblies in aqueous solution due to the disorganized ways in which proteins interact freely under varying conditions such as pH and temperature.
The new method, reported in the journal Chemical Science, overcomes these problems by using protein crystals, which serve as a promising scaffold for proteins to self-assemble into desired structures. The method has four steps, as illustrated in Construction of nanotubes from protein crystals:
- preparation of an engineered protein
- formation of the protein crystal scaffold
- formation of a cross-linked crystal
- release of the protein nanotubes by dissolving the scaffold.
The crystal system, composed of the ordered arrangement of assembled structures, makes it easy to control precise chemical interactions of interest by cross-linking to stabilize the assembly structure — an accomplishment that cannot be achieved from cross-linking of proteins in solution.
The researchers chose a naturally occurring protein called RubisCO as a building block for construction of nanotube. Due to its high stability, RubisCO could keep its shape, and its crystal structure from previous research had recommended it for this study.
Using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) imaging at Tokyo Tech's Suzukakedai Biomaterials Analysis Division, the team successfully confirmed the formation of the protein nanotubes.
The study also demonstrated that the protein nanotubes could retain their enzymatic ability.
“Our cross-linking method can facilitate the formation of the crystal scaffold efficiently at the desired position (specific cysteine sites) within each tubes of the crystal,” says Ueno. “At present, since more than 100,000 protein crystal structures have been deposited in Protein data bank, our method can be applied to other protein crystals for construction of supramolecular protein assemblies, such as cages, tubes, sheets.”
The nanotube in this study can be utilized for various applications. The tube provides the environment for accumulation of the exogenous molecules which can be used as platforms of delivery in pharmaceutical related fields. The tube can also be potential for catalysis because the protein building block has the enzymatic activity in nature.
Related links
Nanocages for gold particles: what is happening inside? https:/
In cell molecular sieve from protein crystal https:/
Crystal Engineering of Self-Assembled Porous Protein Materials in Living Cells https:/
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















