Duplicate or mirror? Laser light determines chirality of molecules
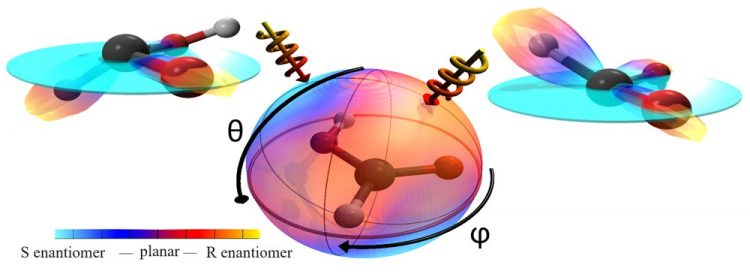
The formic acid model is in the centre. The color code of the surrounding sphere shows the direct chirality of the formic acid for every direction from which the laser comes. If the laser is directed from the right side (right arrow), it results in right-handed formic acid; if from the left, in left-handed formic acid. Both chiral formic acids reflect the common structure of the molecule. Source: www.uni-frankfurt.de/76731281
“In pharmaceutics, being able to transition a molecule from one chirality to the other using light instead of wet chemistry would be a dream,” says Professor Reinhard Dörner from the Institute of Atomic Physics at Goethe University. His doctoral student Kilian Fehre has now brought this dream one step closer to coming true. His observation: the formation of the right- or left-handed version depends on the direction from which laser light hits the initiator.
For his experiment, Kilian Fehre used the planar formic acid molecule. He activated it with an intense, circularly polarized laser pulse to transition it to a chiral form. At the same time, the radiation caused the molecule to break into its atomic components. It was necessary to destroy the molecule for the experiment so that it could be determined whether a duplicate or mirror version was created.
Fehre used the “reaction microscope” (COLTRIMS method) that was developed at the Institute for Atomic Physics for the analysis. It allows the investigation of individual molecules in a molecular beam. After the molecule’s explosive breakdown, the data provided by the detector can be used to precisely calculate the direction and speed of the fragments’ paths. This makes it possible to reconstruct the molecule’s spatial structure.
In order to create chiral molecules with the desired chirality in the future, it has to be ensured that the molecules are oriented the same way with regard to the circularly polarized laser pulse. This could be achieved by orienting them beforehand using a long-wave laser light.
This discovery could also play a critical role in generating larger quantities of molecules with uniform chirality. However, the researchers believe that in such cases, liquids would probably be radiated rather than gases. “There is a lot of work to be done before we get that far,” Kilian Fehre believes.
The detection and manipulation of chiral molecules using light is the focus of a priority programme which goes by the memorable name “ELCH” and which has been funded by the German Research Council since 2018. Scientists from Kassel, Marburg, Hamburg and Frankfurt have joined forces in this programme. “The long-term funding and the close collaboration with the priority programme provide us with the necessary resources to learn to control chirality in a large class of molecules in the future,” concludes Markus Schöffler, one of the Frankfurt project managers of the priority programme.
Publication: K. Fehre, S. Eckart, M. Kunitski, M. Pitzer, S. Zeller, C. Janke, D. Trabert, J. Rist, M. Weller, A. Hartung, L. Ph. H. Schmidt, T. Jahnke, R. Berger, R. Dörner und M. S. Schöffler: Enantioselective fragmentation of an achiral molecule in a strong laser field, in: Science Advances, doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau7923
An image can be downloaded here: www.uni-frankfurt.de/76731281
Caption: The formic acid model is in the centre. The color code of the surrounding sphere shows the direct chirality of the formic acid for every direction from which the laser comes. If the laser is directed from the right side (right arrow), it results in right-handed formic acid; if from the left, in left-handed formic acid. Both chiral formic acids reflect the common structure of the molecule.
Further information: Kilian Fehre, Tel: +49 69 798-47004, fehre@atom.uni-frankfurt.de; Prof. Reinhard Dörner, Tel: +49 69 798-47003, doerner@atom.uni-frankfurt.de; Dr. Markus Schöffler, Tel: +49 69 798-47022, schoeffler@atom.uni-frankfurt.de. Institute for Atomic Physics, Faculty of Physics, Riedberg Campus.
Current news about science, teaching, and society can be found on GOETHE-UNI online (www.aktuelles.uni-frankfurt.de)
Goethe University is a research-oriented university in the European financial centre Frankfurt am Main. The university was founded in 1914 through private funding, primarily from Jewish sponsors, and has since produced pioneering achievements in the areas of social sciences, sociology and economics, medicine, quantum physics, brain research, and labour law. It gained a unique level of autonomy on 1 January 2008 by returning to its historic roots as a “foundation university”. Today, it is one of the three largest universities in Germany. Together with the Technical University of Darmstadt and the University of Mainz, it is a partner in the inter-state strategic Rhine-Main University Alliance. Internet: www.uni-frankfurt.de
Publisher: The President of Goethe University Editor: Dr. Anne Hardy, Science Editor, PR & Communication Department, Theodor-W.-Adorno-Platz 1, 60323 Frankfurt am Main, Tel: (069) 798-13035, Fax: (069) 798-763 12531.
Kilian Fehre, Tel: +49 69 798-47004, fehre@atom.uni-frankfurt.de; Prof. Reinhard Dörner, Tel: +49 69 798-47003, doerner@atom.uni-frankfurt.de; Dr. Markus Schöffler, Tel: +49 69 798-47022, schoeffler@atom.uni-frankfurt.de. Institute for Atomic Physics, Faculty of Physics, Riedberg Campus.
https://aktuelles.uni-frankfurt.de/englisch/physics-laser-light-determines-chira…
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















