Secure communication between quantum computers implemented: The quantum internet is within reach
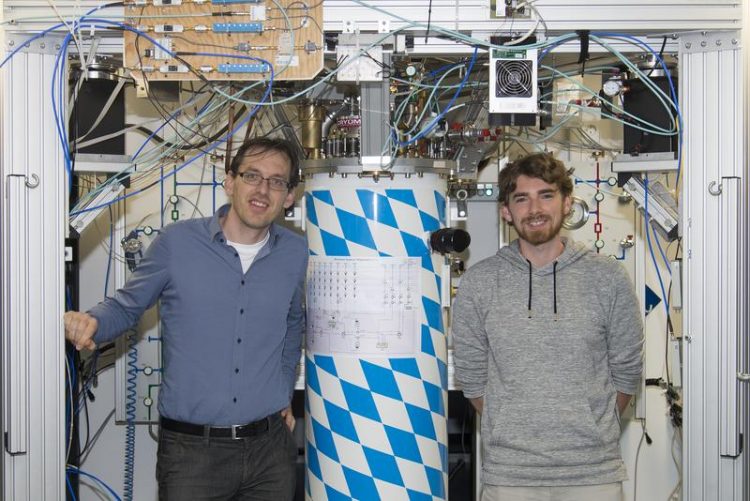
First author Stefan Pogorzalek (r) and co-author Dr. Frank Deppe with the cryostat, in which they have realized a quantum LAN for the first time. Bild: Andreas Battenberg / TUM
As of yet, there are no universal quantum computers in the world. But for the first time, an international team led by TUM physicists Rudolf Gross, Frank Deppe and Kirill Fedorov has successfully implemented secure quantum communication in a local network – via a 35-centimeter superconducting cable.
“We have thus laid the foundation for implementing quantum communication systems in the very important microwave range,” says Rudolf Gross, professor of technical physics at the Technical University of Munich and director of the Walther Meißner Institute (WMI), where the experiments took place.
“This is a milestone. This puts the quantum internet, based on superconducting circuits and microwave communications, within arm’s reach.”
Years of pioneering work
Researchers at WMI have been pioneering the propagation of quantum microwaves for more than a decade. First, they had to prove that microwave radiation even has quantum mechanical properties. Unlike with visible light, this was extremely challenging from a technical point of view, due to the low energy of the microwave photons.
To eliminate interferences, the experiments were done at temperatures near absolute zero. Using special cooling devices, the physicists ultimately succeeded in demonstrating the principle of entanglement in the microwave range, an important prerequisite for reliable quantum communication.
Wiretapping-proof protocol using entanglement
The physicists’ current work brings them one step closer to the actual application: “Quantum Remote State Preparation,” as they call their communication protocol. A quantum state can be set at a remote location without sending anything directly.
The concept can be visualized as follows: Two people, let's call them Alice and Bob, are in two different places. While a bit is the smallest piece of information in classical informatics, in quantum communication it is a quantum state.
Now, if Alice wants to send Bob a piece of information, both are given part of an entangled quantum mechanical state. Alice then does a measurement on her part of the state and transmits the result to Bob via classical means. Bob, in turn, performs a result-dependent operation on his part of the entangled state, thereby obtaining the quantum state that Alice wants to communicate to him.
The classically transmitted measurement result is of no use to any third party since they will not have the entangled state. This makes communications via this protocol absolutely immune to wiretapping.
Information transmission using squeezed waves
The researchers use a so-called squeezed microwave state as the quantum state. This is a special manifestation of an electromagnetic wave that can only be explained with quantum mechanics.
Here, a wave’s vacuum fluctuations are suppressed in one plane and amplified in the plane perpendicular to the first. Two such squeezed states can be used to produce an entangled state. The physicists developed this technique and other important details, such as superconducting quantum circuits, at the Walther Meißner Institute in Garching.
Seven-meter, cooled quantum cable
The new concept could trigger a revolutionary development. “The experimental implementation of secure quantum communication in the microwave domain is an important step towards distributed quantum computing,” says Frank Deppe, WMI coordinator of the European flagship project Quantum Microwave Communication and Sensing (QMiCS).
The TUM physicists also believe that significantly longer distances are possible between quantum computers. Here, one challenge will be to develop and measure several meters of cooled quantum cables. “In the context of QMiCS, we are already working on extending the distance to seven meters,” says Gross. “This puts networking of superconducting quantum computers within reach.”
Further information:
The research was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG), the Cluster of Excellence “Munich Center for Quantum Science and Technology” (MCQST), the doctoral program ExQM of the Elite Network of Bavaria, by the European Union within the flagship projects QMiCS and OpenSuperQ and through Spanish and Japanese funding programs. The Walter Meißner Institute for Low Temperature Physics is a facility of the Bavarian Academy of Sciences (BAdW).
Prof. Dr. Rudolf Gross
Technical University of Munich –Department of Physics and
Walther-Meißner-Institute of the Bavarian Academy of Sciences and Humanities
Walther-Meißner-Str. 6
85748 Garching, Germany
Tel.: +49 89 289 14201 – E-Mail: Rudolf.Gross@wmi.badw.de
Secure quantum remote state preparation of squeezed microwave states
S. Pogorzalek, K. G. Fedorov, M. Xu, A. Parra-Rodriguez, M. Sanz, M. Fischer, E. Xie, K. Inomata, Y. Nakamura, E. Solano, A. Marx, F. Deppe, R. Gross
Nature Communications, Bd. 10, Artikelnr. 2604, (2019), DOI: 10.1063/1.5052414
Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-10727-7
https://www.tum.de/nc/en/about-tum/news/press-releases/details/35764/ Link to the press release
https://www.mcqst.de/ Munich Center for Quantum Science and Technology (MCQST)
https://qmics.wmi.badw.de/ EU Quantum Flagship Projekt QMiCS
https://www.wmi.badw.de WMI
https://www.badw-muenchen.de/ BAdW
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

Peptides on Interstellar Ice
A research team led by Dr Serge Krasnokutski from the Astrophysics Laboratory at the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy at the University of Jena had already demonstrated that simple peptides…

A new look at the consequences of light pollution
GAME 2024 begins its experiments in eight countries. Can artificial light at night harm marine algae and impair their important functions for coastal ecosystems? This year’s project of the training…

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…





















