A nanotech sensor that turns molecular fingerprints into bar codes
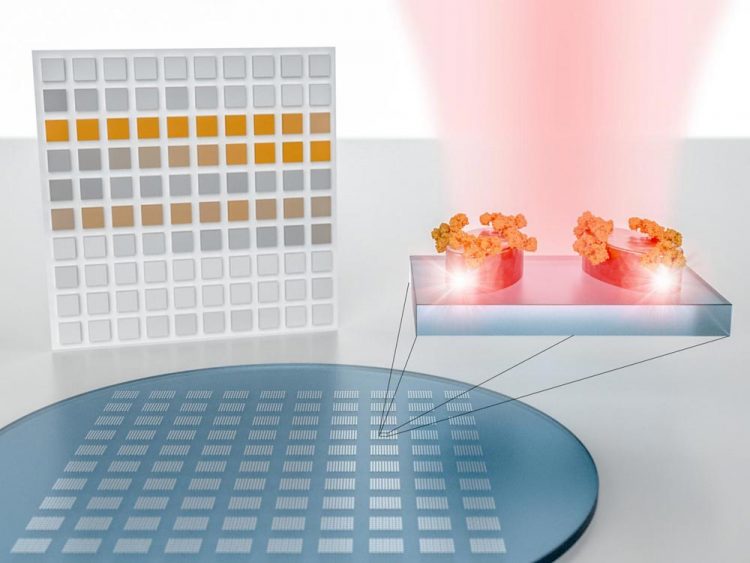
The authors show a pixelated sensor metasurface for molecular spectroscopy. It consists of metapixels designed to concentrate light into nanometer-sized volumes in order to amplify and detect the absorption fingerprint of analyte molecules at specific resonance wavelengths. Simultaneous imaging-based read-out of all metapixels provides a spatial map of the molecular absorption fingerprint sampled at the individual resonance wavelengths. This pixelated absorption map can be seen as a two-dimensional barcode of the molecular fingerprint, which encodes the characteristic absorption bands as distinct features of the resulting image. Credit: EPFL
However, scientists at EPFL's School of Engineering and at Australian National University (ANU) have developed a compact and sensitive nanophotonic system that can identify a molecule's absorption characteristics without using conventional spectrometry.
Their system consists of an engineered surface covered with hundreds of tiny sensors called metapixels, which can generate a distinct bar code for every molecule that the surface comes into contact with. These bar codes can be massively analyzed and classified using advanced pattern recognition and sorting technology such as artificial neural networks. This research – which sits at the crossroads of physics, nanotechnology and big data – has been published in Science.
Translating molecules into bar codes
The chemical bonds in organic molecules each have a specific orientation and vibrational mode. That means every molecule has a set of characteristic energy levels, which are commonly located in the mid-infrared range – corresponding to wavelengths of around 4 to 10 microns. Therefore, each type of molecule absorbs light at different frequencies, giving each one a unique “signature.” Infrared spectroscopy detects whether a given molecule is present in a sample by seeing if the sample absorbs light rays at the molecule's signature frequencies. However, such analyses require lab instruments with a hefty size and price tag.
The pioneering system developed by the EPFL scientists is both highly sensitive and capable of being miniaturized; it uses nanostructures that can trap light on the nanoscale and thereby provide very high detection levels for samples on the surface. “The molecules we want to detect are nanometric in scale, so bridging this size gap is an essential step,” says Hatice Altug, head of EPFL's BioNanoPhotonic Systems Laboratory and a coauthor of the study.
The system's nanostructures are grouped into what are called metapixels so that each one resonates at a different frequency. When a molecule comes into contact with the surface, the way the molecule absorbs light changes the behavior of all the metapixels it touches.
“Importantly, the metapixels are arranged in such a way that different vibrational frequencies are mapped to different areas on the surface,” says Andreas Tittl, lead author of the study.
This creates a pixelated map of light absorption that can be translated into a molecular bar code – all without using a spectrometer.
The scientists have already used their system to detect polymers, pesticides and organic compounds. What's more, their system is compatible with CMOS technology.
“Thanks to our sensors' unique optical properties, we can generate bar codes even with broadband light sources and detectors,” says Aleksandrs Leitis, a coauthor of the study.
There are a number of potential applications for this new system. “For instance, it could be used to make portable medical testing devices that generate bar codes for each of the biomarkers found in a blood sample,” says Dragomir Neshev, another coauthor of the study.
Artificial intelligence could be used in conjunction with this new technology to create and process a whole library of molecular bar codes for compounds ranging from protein and DNA to pesticides and polymers. That would give researchers a new tool for quickly and accurately spotting miniscule amounts of compounds present in complex samples.
###
Source:
Andreas Tittl, Aleksandrs Leitis, Mingkai Liu, Filiz Yesilkoy, Duk-Yong Choi, Dragomir N. Neshev, Yuri S. Kivshar, and Hatice Altug, “Imaging-based molecular barcoding with pixelated dielectric metasurfaces,” Science
BioNanoPhotonic Systems Laboratory (BIOS) / Interfaculty Institute of Bioengineering IBI / School of Engineering – School of Life Sciences / EPFL Nonlinear Physics Centre, Research School of Physics and Engineering, Australian National University, Canberra
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















