Ushering in ultrafast cluster electronics
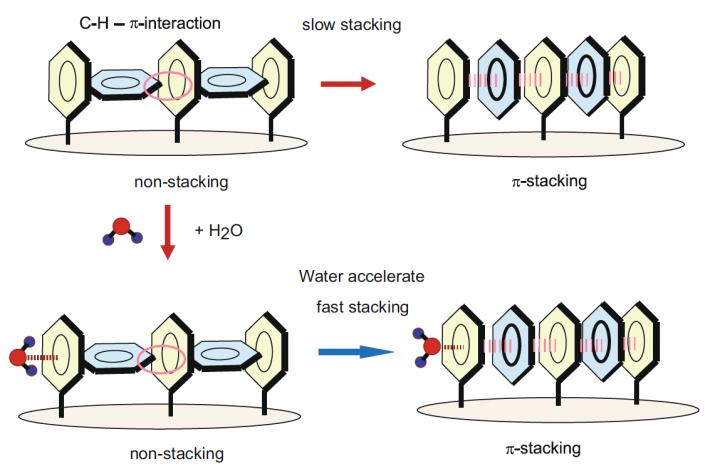
When light is applied to the T-shaped benzene cluster in their computer simulation, they reorganized themselves into a single stack, changing its electrical conductivity. The addition of a molecule of water made the stacking occur significantly faster. Credit: Tachikawa H., et al. Scientific Reports, Feb. 20, 2019 Usage Restrictions: This image is copyrighted and can be used for reporting this press release if appropriately credited.
Hokkaido University researchers have developed a computational method that can predict how clusters of molecules behave and interact over time, providing critical insight for future electronics. Their findings, published in the journal Scientific Reports, could lead to the creation of a new field of science called cluster molecular electronics.
Single molecule electronics is a relatively new, rapidly progressing branch of nanotechnology using individual molecules as electronic components in devices.
Now, Hiroto Tachikawa and colleagues at Hokkaido University in Japan have developed a computational approach that can predict how clusters of molecules behave over time, which could help launch a new field of study for cluster molecule electronics. Their approach combines two methods traditionally used for quantum chemical and molecular dynamic calculations.
They used their method to predict the changes in a computer-simulated cluster of benzene molecules over time. When light is applied to the T-shaped benzene clusters, they reorganize themselves into a single stack; an interaction known as pi-stacking.
This modification from one shape to another changes the cluster's electrical conductivity, making it act like an on-off switch. The team then simulated the addition of a molecule of water to the cluster and found that pi-stacking happened significantly faster. This pi-stacking is also reversible, which would allow switching back and forth between the on and off modes.
In contrast, previous studies had shown that the addition of a molecule of water to a single molecule electronic device impedes its performance.
“Our findings could usher in a new field of study that investigates the electronic performance of different numbers, types and combinations of molecular clusters, potentially leading to the development of cluster molecule electronic devices,” Tachikawa commented.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















