University of Minnesota engineers make sound loud enough to bend light on a computer chip
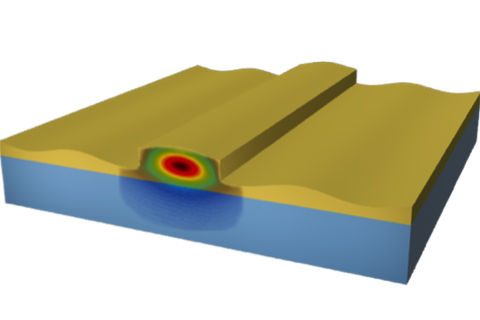
The figure illustrates a sound wave passing across an integrated optical waveguide, overlaid with a color map of the light field in it.
During a thunderstorm, we all know that it is common to hear thunder after we see the lightning. That’s because sound travels much slower (768 miles per hour) than light (670,000,000 miles per hour).
Now, University of Minnesota engineering researchers have developed a chip on which both sound wave and light wave are generated and confined together so that the sound can very efficiently control the light. The novel device platform could improve wireless communications systems using optical fibers and ultimately be used for computation using quantum physics.
The research was recently published in Nature Communications, a leading research journal.
The University of Minnesota chip is made with a silicon base coated with a layer of aluminum nitride that conducts an electric change. Applying alternating electrical signal to the material causes the material to deform periodically and generate sound waves that grow on its surface, similar to earthquake waves that grow from the center of the earthquake. The technology has been widely used in cell phones and other wireless devices as microwave filters.
“Our breakthrough is to integrate optical circuits in the same layer of material with acoustic devices in order to attain extreme strong interaction between light and sound waves,” said Mo Li, assistant professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and the lead researcher of the study.
The researchers used the state-of-the-art nanofabrication technology to make arrays of electrodes with a width of only 100 nanometers (0.00001 centimeters) to excite sound waves at an unprecedented high frequency that is higher than 10 GHz, the frequency used for satellite communications.
“What’s remarkable is that at this high frequency, the wavelength of the sound is even shorter than the wavelength of light. This is achieved for the first time on a chip,” said Semere Tadesse, a graduate student in the University of Minnesota’s School of Physics and Astronomy and the first author of the paper. “In this unprecedented regime, sound can interact with light most efficiently to achieve high-speed modulation.”
In addition to applications in communications, researchers are pursuing quantum physics applications for the novel device. They are investigating the interaction between single photons (the fundamental quantum unit of light) and single phonons (the fundamental quantum unit of sound). The researcher plan to use sound waves as the information carriers for quantum computing.
The research is funded by National Science Foundation and Air Force Office of Scientific Research. The device was fabricated in the cleanroom at the Minnesota Nano Center at the University of Minnesota.
To read the full article, entitled “Sub-optical wavelength acoustic wave modulation of integrated photonic resonators at microwave frequencies,” visit the Nature Communications website.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















