Stabilizing shell effects in heaviest elements directly measured
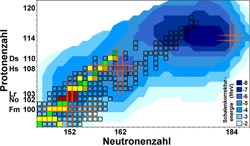
Chart of nuclides in the region of the heaviest elements. This map shows presently known isotopes of the heaviest elements as squares. Blue: calculated strength of shell effects. Red: nobelium and lawrencium isotopes studied. Green / yellow: Nuclides whose masses have been improved by the results. Orange: Location of closed shells.<br><br>Credit: Courtesy of Science/AAAS<br>
An international research team has succeeded in directly measuring the strength of shell effects in very heavy elements. The results provide information on the nuclear structure of superheavy elements, thus promising to enable improved predictions concerning the location and extension of the island of stability of superheavy elements. Indeed, it is expected that this group of elements will profit from enhanced stability due to shell effects, which endow them with long lifetimes. The exact location of this island is still a topic of intense discussions.
For the present measurements, performed on several isotopes of the elements nobelium und lawrencium, the scientists utilized the Penning trap facility SHIPTRAP at the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research in Darmstadt. The results have been published in the renowned Science magazine.
So-called “superheavy” elements owe their very existence exclusively to shell effects within the atomic nucleus. The building blocks of an atomic nucleus, protons and neutrons, organize themselves in shells. Certain “magic” configurations with completely filled shells render the protons and neutrons to be more strongly bound together. Without this stabilizing effect atomic nuclei of superheavy elements would disintegrate in a split second due to the strong repulsion between their many protons.
Long-standing theoretical predictions suggest that in superheavy elements, filled proton and neutron shells will give rise to extraordinarily stable and hence long-lived nuclei: the “Island of stability“. Still, after decades of research, its exact location on the chart of nuclei is a topic of intense discussions and no consensus has yet been reached. While some theoretical models predict a magic proton number to be at element 114, others prefer element 120 or even 126. Another burning question is whether nuclei situated on the island will live “only“ hundreds or maybe thousands or even millions of years. Anyway, all presently known superheavy elements were created in the laboratory and are short-lived. No superheavy elements have been found in nature yet.
Precise information on the strength of shell effects that enhance binding energies of protons and neutrons for filled shells is a key ingredient for more accurate theoretical predictions. As the binding energy is directly related to the mass via Einstein’s famous equation E=mc2, the weighing of nuclei provides access to the nuclear binding energies and thus the strength of the shell effects. With the ion-trap facility SHIPTRAP, presently the most precise balance for weighing the heaviest elements, a series of very heavy atomic nuclei in the region of the magic neutron number N=152 have now been weighed with utmost precision for the first time. The studies at hand focused on nobelium (element 102) and lawrencium (element 103). These elements do not exist in nature, so the scientists produced them at the GSI’s particle accelerator facility and captured them in the SHIPTRAP. The measurements had to be performed with just a handful of atoms: for the isotope lawrencium-256 only about 50 could be studied during a measurement time of about four days.
The new data will benchmark the best present models for the heaviest atomic nuclei and provide an important stepping stone to further refining the models. This will lead to more precise predictions on the location and extension of the island of stability of superheavy elements.
The experiments were carried out by an international team led by scientists of GSI and the 2009 established Helmholtz-Institute Mainz (HIM), a joint institution of the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy Ion Research, Darmstadt, and the Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, in collaboration with scientists from the universities of Giessen, Granada (Spain), Greifswald, Heidelberg, Mainz, Munich und Padua (Italy), as well as the Max-Planck-Institute for Nuclear Physics Heidelberg and the PNPI St. Petersburg (Russia).
Scientific Contacts:
Dr. Michael Block
GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research
Planckstrasse 1
64291 Darmstadt
http://www.gsi.de
Prof. Dr. Christoph E. Düllmann
Helmholtz Institute Mainz and Institute for Nuclear Chemistry
Johannes Gutenberg University
55099 Mainz
http://www.helmholtz.de/en/research/promoting_research/helmholtz_
institutes/helmholtz_institute_mainz
http://www.kernchemie.uni-mainz.de/eng/index.php
Prof. Dr. Klaus Blaum
Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik
Saupfercheckweg 1
69117 Heidelberg
http://www.mpi-hd.mpg.de/
Prof. Dr. Lutz Schweikhard
Institute of Physics
Ernst-Moritz-Arndt-University Greifswald
17487 Greifswald
http://www.physik.uni-greifswald.de/physik01
Priv. Doz. Dr. Peter G. Thirolf
Department of Physics
Ludwig-Maximilians-University
Am Coulombwall 1
85748 Garching
http://www.en.physik.uni-muenchen.de/index.html
Dr. Wolfgang Plaß
II. Physics Institute
Justus-Liebig University
Heinrich-Buff-Ring 14
35392 Gießen
http://pcweb.physik.uni-giessen.de/exp2/
Weitere Informationen:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1225636
E. Minaya Ramirez et al. “Direct mapping of nuclear shell effects in the heaviest elements”, Science 2012
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.gsi.deAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















