Dark matter mystery deepens in cosmic 'train wreck'
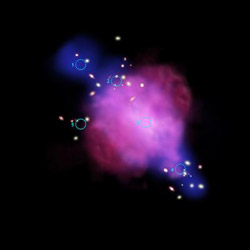
An artist's illustration of the Abell 520 system shows where the bulk of the matter (blue) is found compared to the individual galaxies (yellow) and the hot gas (red) in the aftermath of a massive galaxy cluster collision. The material shown in blue is dominated by dark matter. As with the Bullet Cluster there are large separation between the regions where the galaxies are most common (peaks 2 and 4) and where most of the hot gas lies (peak 3). However, unlike the Bullet Cluster, a concentration of dark matter is found (peak 3) near the bulk of the hot gas, where very few galaxies are located. In addition, there is an area (peak 5) where there are several galaxies but very little dark matter. These observations conflict with the general understanding that dark matter and the galaxies should remain together, despite a violent collision. This raises questions about the current understanding of how dark matter behaves. Credit: CXC/M. Weiss
These results challenge our understanding of the way clusters merge,” said Dr. Andisheh Mahdavi of the University of Victoria, British Columbia. “Or, they possibly make us even reexamine the nature of dark matter itself.”
There are three main components to galaxy clusters: individual galaxies composed of billions of stars, hot gas in between the galaxies, and dark matter, a mysterious substance that dominates the cluster mass and can be detected only through its gravitational effects.
Optical telescopes can observe the starlight from the individual galaxies, and can infer the location of dark matter by its subtle light-bending effects on distant galaxies. X-ray telescopes like Chandra detect the multimillion-degree gas.
A popular theory of dark matter predicts that dark matter and galaxies should stay together, even during a violent collision, as observed in the case of the so-called Bullet Cluster. However, when the Chandra data of the galaxy cluster system known as Abell 520 was mapped along with the optical data from the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope and Subaru Telescope atop Mauna Kea, HI, a puzzling picture emerged. A dark matter core was found, which also contained hot gas but no bright galaxies.
“It blew us away that it looks like the galaxies are removed from the densest core of dark matter,” said Dr. Hendrik Hoekstra, also of University of Victoria. “This would be the first time we've seen such a thing and could be a huge test of our knowledge of how dark matter behaves.”
In addition to the dark matter core, a corresponding “light region” containing a group of galaxies with little or no dark matter was also detected. The dark matter appears to have separated from the galaxies.
“The observation of this group of galaxies that is almost devoid of dark matter flies in the face of our current understanding of the cosmos,” said Dr. Arif Babul, University of Victoria. “Our standard model is that a bound group of galaxies like this should have a lot of dark matter. What does it mean that this one doesn't””
In the Bullet Cluster, known as 1E 0657-56, the hot gas is slowed down during the collision but the galaxies and dark matter appear to continue on unimpeded. In Abell 520, it appears that the galaxies were unimpeded by the collision, as expected, while a significant amount of dark matter has remained in the middle of the cluster along with the hot gas.
Mahdavi and his colleagues have two possible explanations for their findings, both of which are uncomfortable for prevailing theories. The first option is that the galaxies were separated from the dark matter through a complex set of gravitational “slingshots.” This explanation is problematic because computer simulations have not been able to produce slingshots that are nearly powerful enough to cause such a separation.
The second option is that dark matter is affected not only by gravity, but also by an as-yet-unknown interaction between dark matter particles. This exciting alternative would require new physics and could be difficult to reconcile with observations of other galaxies and galaxy clusters, such as the aforementioned Bullet Cluster.
In order to confirm and fully untangle the evidence for the Abell 520 dark matter core, the researchers have secured time for new data from Chandra plus the Hubble Space Telescope. With the additional observations, the team hopes to resolve the mystery surrounding this system.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.cfa.harvard.eduAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















