Bones at the nanoscale – Scientists see with X-rays how bones resist strain thanks to their nano and micro structure
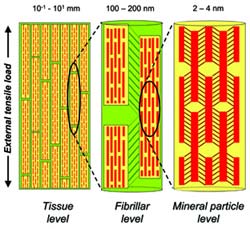
The hierarchical structure of bone gives rise to a hierarchical deformation via a staggered load transfer mechanism at the nanoscale. The yellow cylinders denote the mineralized collagen fibrils in longitudinal section, and the red tablets denote the mineral apatite crystallites embedded within the collageneous matrix of the fibrils. The strain decreases from the tissue (left) to mineral particle level (right) in a ratio of approximately 12:5:2. Credits: Himadri Gupta/Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces.
A bone is made up of two different elements: half of it is a stretchable fibrous protein called collagen and the other half a brittle mineral phase called apatite. These components make this biomineralized tissue highly strong and tough. at the same time, In order to understand how this construction is achieved and functions, scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces in Potsdam (Germany) came to the ESRF. Using X-rays they were able to see for the first time the simultaneous re-arrangement of organic and inorganic components at a micro and nanoscale level under tensile stress.
The scientists realised that when strain/pressure is applied to a bone, this is absorbed by soft layers at successively lower length scales, and less than a fifth of the strain is actually noticed in the mineral phase. The soft structures form a single rigid unit at the next level and so on, enabling the tissue to sustain large strains. This is why the brittle apatite remains shielded from excessive loads and does not break.
The results also showed that the mineral crystallites are nonetheless very strong, capable of carrying more than 2 – 3 times the fracture load of bulk apatite. Their small size preserves them from large cracks. This is the first experimental evidence for this effect in biomaterials – small particles resist failure better.
Scientists carried out experiments on ID2 beamline at the ESRF. They tracked the molecular and supramolecular rearrangements in bone while they applied stress using the techniques of X-ray scattering and diffraction in real time. The high brilliance of the X-ray source enabled the tracking of bone deformation in real time. Researchers could look at two length scales: on one side they observed the 100 nanometers sized fibres, and on the other, the crystallites embedded inside the fibre, which are not bigger than 2 to 4 nanometers. The critical sample preparation was developed by Max Planck researchers, which made it possible to isolate tissue in bone of about 100-200 microns of size.
These results provide new insight in the design principles which make healthy bone so fracture resistant. The research may contribute to medical as well as technological developments: “The outcome of this research may contribute to a future development of bio-inspired and new nanocomposite materials. On a medical level, it may help to understand how a molecular level change can make whole bones more prone to fracture in diseases like osteoporosis”, explains Himadri Gupta, first author of the paper. Further ongoing research aims at telling us how these design principles differ in bones with different mechanical function and how they may be affected by age and disease.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.esrf.fr/news/pressreleases/bones/All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















