French-German Group Verifies High-Temperature Superconductivity Theory Proposed by UCR Physicist
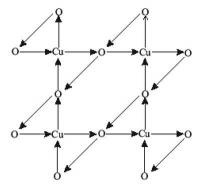
A 1996 theory by UCR’s Chandra Varma notes that in copper oxide materials superconductivity is associated with the formation of a new state of matter in which electric current loops form spontaneously, going from copper to oxygen atoms and back to copper. Recently, a French-German team of experimental scientists directly observed the current loops. Credit: C. Varma
Experimental results could point the way to fabricating room temperature superconductors and solving a major mystery in physics
A French-German team of experimental scientists, led by Philippe Bourges of the Commissariat à l’Energie Atomique, France, reports that it has verified the central prediction of a theory on high-temperature superconductivity developed by Chandra Varma, distinguished professor of physics at UC Riverside. The verification ultimately could assist in the fabrication of materials that are superconducting at room temperature and help settle a contentious, international debate on the fundamental physics of superconductivity and emergent states of matter.
Varma’s initial theory, which he proposed in 1989 when he was at Bell Laboratories, stated the radical idea that high temperature superconductivity and related phenomena occur in certain materials because quantum-mechanical fluctuations in these materials increase as temperature decreases. Usually such fluctuations, which determine the properties of all matter in the universe, decrease as temperature decreases.
Varma’s theory did not explain the nature of the fluctuations; he accomplished this in a theory he proposed in 1996, while still at Bell Labs, in which he noted that in copper oxide materials, also known as cuprates, superconductivity is associated with the formation of a new state of matter in which electric current loops form spontaneously, going from copper to oxygen atoms and back to copper. His theory concluded that the quantum-mechanical fluctuations are the fluctuations of these current loops. Physicists consider these fluctuations in the current loops to be fluctuations of time.
Bourges’s group directly observed the current loops in experiments involving the diffraction of polarized neutrons. In these experiments a beam of neutrons changes direction as well as the direction of its magnetization in a manner that is closely related to the geometrical arrangement of the current loops inside the material in which the beam is made to pass.
“Currently, there is much debate among researchers working on superconductivity about what exactly happens in cuprates,” said Varma, who joined UCR in 2003 and was a Bell Labs researcher from 1969 to 2001. “Further experiments of the kind by Bourges’s group should help bring a consensus in the scientific community about the fundamental physics involved in cuprates.”
The results of Bourges’s experiments appear in the May 19 issue of Physical Review Letters.
“Chandra Varma has been a pioneer in the theory of high-temperature superconductivity since its discovery 20 years ago, and Bell Labs is delighted to see confirmation of his microscopic theory by the neutron scattering experiments of Bourges and coworkers,” said Arthur Ramirez, director of Device Physics Research at Lucent Technologies Bell Labs. “The confirmation of this theory could become a turning point for research we and other laboratories are performing on high-temperature superconductivity.”
Before Bourges’s group observed the current loops Varma predicted, an experiment performed in 2002 by a group of scientists at Argonne National Laboratory and the University of Illinois, Chicago, discovered the current loops in an indirect way by using an experimental technique Varma suggested in 2000.
“The fact that two experiments came to the same conclusion with different techniques and in different cuprate compounds lends great confidence in the results,” said Harry Tom, chair of the Department of Physics at UCR. “A microscopic theory of high temperature superconductivity might also suggest ways of fabricating room temperature superconductors, possibly with materials more amenable to industrial fabrication than the cuprates.”
Superconductors are materials that conduct electricity with near-zero resistance below a specific temperature, known as the critical temperature. Superconductors typically find use in electric power transformers and magnetic resonance imaging machines. Conventional metallic superconductors must be cooled below -424 F to become superconducting.
High-temperature superconductors, which are almost always some type of cuprate ceramic doped with a variety of elements, conduct electricity with near-zero resistance at temperatures as high as -226 F.
High-temperature superconductivity in compounds of copper, oxygen and other elements were discovered in 1986 by Swiss scientists, Georg Bednorz and Alex Müller. Both scientists were awarded the 1987 Nobel Prize in physics “for their important break-through in the discovery of superconductivity in ceramic materials.”
“While our results are exciting, our specific approach needs to be checked by another neutron group,” said Bourges. “My group plans to design refined experiments to improve the data and verify the theory in more detail.”
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.ucr.eduAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















