Arsia Mons volcano in 3D
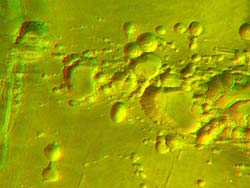
Arsia Mons volcano in 3D <br>Credits: ESA/DLR/FU (G. Neukum)
This image of the Arsia Mons shield volcano was taken by the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) on board ESA’s Mars Express.
This image shows a spectacular zone of collapse features on the southern flank of the giant shield volcano Arsia Mons (located at 239°E longitude and 10°S latitude, see the Mars map image).
The image was taken from an altitude of about 400 kilometres during orbit 263 of the Mars Express spacecraft.
The original image resolution was 20 metres per pixel, but the versions shown here have been reprocessed to reduce the volume of data for use on the internet.
The main red-green anaglyph image, covering an area of 38 kilometres by 53 kilometres, is a detail section of the top left of the black and white image below, which covers an area of 80 kilometres by 105 kilometres.
The total height difference in the land surfaces in these scenes is about 7 kilometres, and some individual collapse pits have a depth of 2 kilometres.
The pits probably formed when lava erupted from the side of Arsia Mons. When lava, or molten rock, finds its way to the surface, it produces several veins and chambers. These slowly empty as the lava erupts and runs down the volcano flanks.
Some of the lava reaching the surface cools down and becomes solid, often building a roof over the emptied chamber. The resulting voids collapse due to the weight of the overlying material. At several places, the walls of the pits have been modified by later landslides.
The overall trend of the collapse zone runs from the south-west to the north-east, following exactly a giant zone of crustal weakness in the Tharsis region, along which the three large volcanoes Arsia, Pavonis and Ascraeus Montes are aligned.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.esa.int/SPECIALS/Mars_Express/SEM2EAHHZTD_0.htmlAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















