SOHO snaps spectacular Sun shot
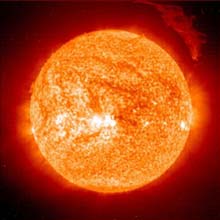
SOHO sees eruptive prominence <br>Credits: ESA/NASA
On Friday, 12 March 2004, the Sun ejected a spectacular ’eruptive prominence’ into the heliosphere. SOHO, the ESA/NASA solar watchdog observatory, faithfully recorded the event.
This ’eruptive prominence’ is a mass of relatively cool plasma, or ionised gas. We say ’relatively’ cool, because the plasma observed by the Extreme-ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (EIT) on board SOHO was only about 80 000 degrees Celsius, compared to the plasma at one or two million degrees Celsius surrounding it in the Sun’s tenuous outer atmosphere, or ’corona’.
At the time of this snapshot, the eruptive prominence seen at top right was over 700 000 kilometres across – over fifty times Earth’s diameter – and was moving at a speed of over 75 000 kilometres per hour.
Eruptive prominences of this size are associated with coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and the combination of CMEs and prominences can affect Earth’s magnetosphere when directed toward our planet. In this case, the eruptive prominence and associated CME were directed away from Earth.
SOHO is a mission of international co-operation between ESA and NASA, launched in December 1995. Every day SOHO sends thrilling images from which research scientists learn about the Sun’s nature and behaviour. Experts around the world use SOHO images and data to help them predict ’space weather’ events affecting our planet.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.esa.int/esaSC/SEMBYM8CURD_extreme_0.htmlAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















