Quantum 'spooky action at a distance' becoming practical
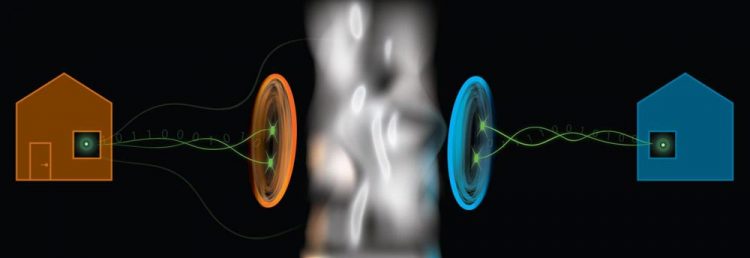
Scientists from Griffith University (Australia) have overcome a major challenge connected to Einstein's 'spooky action at a distance' effect. Credit: Griffith University
A team from Griffith's Centre for Quantum Dynamics in Australia have demonstrated how to rigorously test if pairs of photons – particles of light – display Einstein's “spooky action at a distance”, even under adverse conditions that mimic those outside the lab.
They demonstrated that the effect, also known as quantum nonlocality, can still be verified even when many of the photons are lost by absorption or scattering as they travel from source to destination through an optical fiber channel. The experimental study and techniques are published in the journal Science Advances.
Quantum nonlocality is important in the development of new global quantum information networks, which will have transmission security guaranteed by the laws of physics. These are the networks where powerful quantum computers can be linked.
Photons can be used to form a quantum link between two locations by making a pair of photons that are “entangled” – so that measuring one determines the properties of its twin – and then sending one along a communication channel.
Team leader Professor Geoff Pryde said a quantum link had to pass a demanding test that confirmed the presence of quantum nonlocality between particles at either end.
“Failing the test means an eavesdropper might be infiltrating the network,” he said.
“As the length of quantum channel grows, less and less photons successfully pass through the link, because no material is perfectly transparent and absorption and scattering take their toll.
“This is a problem for existing quantum nonlocality verification techniques with photons. Every photon lost makes it easier for the eavesdropper to break the security by mimicking entanglement.”
Developing a method to test entanglement in presence of loss has been an outstanding challenge for the scientific community for quite some time.
The team used a different approach – quantum teleportation – to overcome the problem of lost photons.
Dr Morgan Weston, first author of the study, said they selected the few photons that survived the high-loss channel and teleported those lucky photons into another clean and efficient, quantum channel.
“There, the chosen verification test, called quantum steering, could be done without any problem,” she said.
“Our scheme records an additional signal that lets us know if the light particle has made it through the transmission channel. This means that the failed distribution events can be excluded up front, allowing the communication to be implemented securely even in the presence of very high loss.”
This upgrade doesn't come easy – the teleportation step requires additional high-quality photon pairs on its own. These extra photon pairs have to be generated and detected with extremely high efficiency, in order to compensate for the effect of the lossy transmission line.
This was possible to achieve thanks to state of art photon source and detection technology, jointly co-developed with the US National Institute of Standards and Technology in Boulder, Colorado.
Although the experiment was performed in the laboratory, it tested channels with photon absorption equivalent to about 80 km of telecommunications optical fiber.
The team aims to integrate their method into quantum networks that are being developed by the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology, and test it in real-life conditions.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















