Quantum sensor for photons
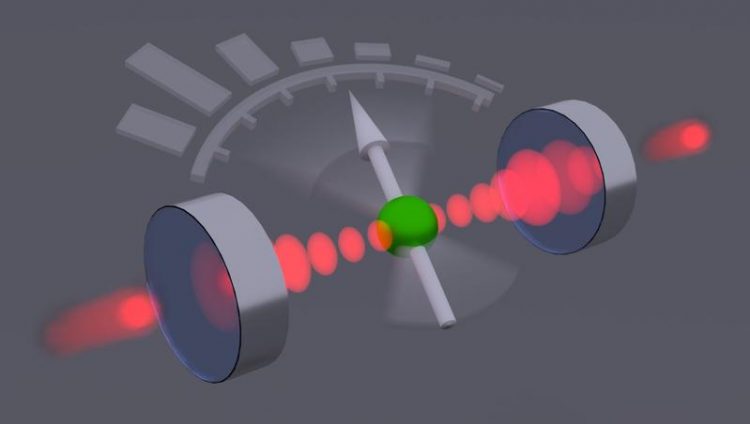
An ion between two spherical mirrors serves as a quantum sensor for light particles. Klemens Schüppert
Physicist Tracy Northup is currently researching the development of quantum internet at the University of Innsbruck. The American citizen builds interfaces with which quantum information can be transferred from matter to light and vice versa.
Over such interfaces, it is anticipated that quantum computers all over the world will be able to communicate with each other via fiber optic lines in the future. In their research, Northup and her team at the Department of Experimental Physics have now demonstrated a method with which visible light can be measured non-destructively.
The development follows the work of Serge Haroche, who characterized the quantum properties of microwave fields with the help of neutral atoms in the 1990s and was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2012.
In work led by postdoc Moonjoo Lee and PhD student Konstantin Friebe, the researchers place an ionized calcium atom between two hollow mirrors through which visible laser light is guided. “The ion has only a weak influence on the light,” explains Tracy Northup.
“Quantum measurements of the ion allow us to make statistical predictions about the number of light particles in the chamber.” The physicists were supported in their interpretation of the measurement results by the research group led by Helmut Ritsch, a Innsbruck quantum optician from the Department of Theoretical Physics.
“One can speak in this context of a quantum sensor for light particles”, sums up Northup, who has held an Ingeborg Hochmair professorship at the University of Innsbruck since 2017. One application of the new method would be to generate special tailored light fields by feeding the measurement results back into the system via a feedback loop, thus establishing the desired states.
In the current work in Physical Review Letters, the researchers have limited themselves to classical states. In the future, this method could also be used to measure quantum states of light. The work was financially supported by the Austrian Science Fund FWF and the European Union, among others.
Tracy Northup
Department of Experimental Physics
University of Innsbruck
phone: +43 512 507 52463
email: tracy.northup@uibk.ac.at
web: https://quantumoptics.at/
Ion-based nondestructive sensor for cavity photon numbers. Moonjoo Lee, Konstantin Friebe, Dario A. Fioretto, Klemens Schüppert, Florian R. Ong, David Plankensteiner, Valentin Torggler, Helmut Ritsch, Rainer Blatt, and Tracy E. Northup. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 153603 https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.122.153603
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uibk.ac.atAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















