Novel approach to coherent control of a three-level quantum system
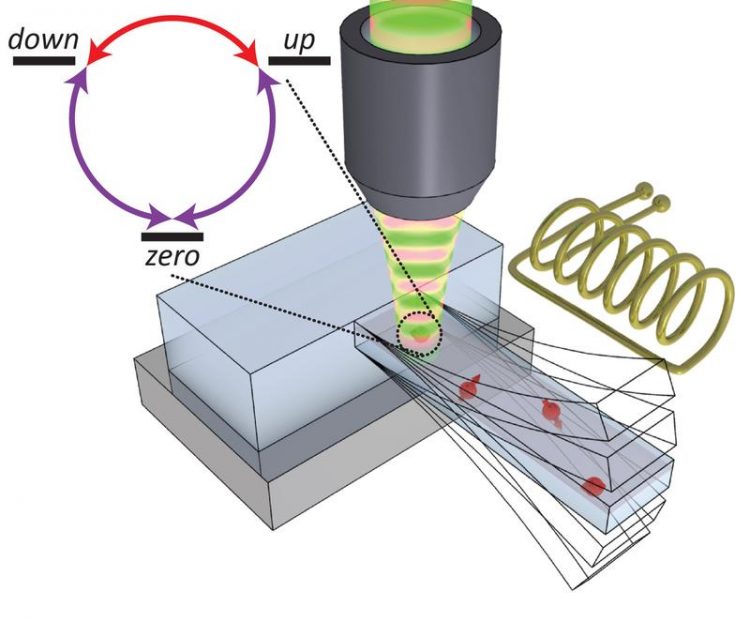
The oscillating cantilever influences the spin of the electrons in the nitrogen-vacancy centers (red arrows). The phase of the oscillator determined in which direction the spin rotates. Illustration: University of Basel / Swiss Nanoscience Institute
The electronic spin is a fundamental quantum mechanical property intrinsic to every electron. In the quantum world, the electronic spin describes the direction of rotation of the electron around its axis which can normally occupy two so-called eigenstates commonly denoted as “up” and “down.” The quantum properties of such spins offer interesting perspectives for future technologies, for example in the form of extremely precise quantum sensors.
Combining spins with mechanical oscillators
Researchers led by Professor Patrick Maletinsky and PhD candidate Arne Barfuss from the Swiss Nanoscience Institute at the University of Basel report in Nature Physics a new method to control the spins’ quantum behavior through a mechanical system.
For their experimental study, they combined such a quantum system with a mechanical oscillator. More specifically, the researchers employed electrons trapped in so-called nitrogen-vacancy centers and embedded these spins in single-crystalline mechanical resonators made from diamond.
These nitrogen-vacancy spins are special, in that they possess not only two, but three eigenstates, which can be described as “up,” “down” and “zero.” Using the special coupling of a mechanical oscillator to the spin, they showed for the first time a complete quantum control over such a three-level system, in a way not possible before.
Controlling three quantum states
In particular, the oscillator allowed them to address all three possible transitions in the spin and to study how the resulting excitation pathways interfere with each other.
This scenario, known as “closed-contour driving,” has never been investigated so far but opens interesting fundamental and practical perspectives. For example, their experiment allowed for a breaking of time-reversal symmetry, which means that the properties of the system look fundamentally different if the direction of time is reversed than without such inversion. In this scenario, the phase of the mechanical oscillator determined whether the spin circled “clockwise” (direction of rotation up, down, zero, up) or “counter-clockwise.”
Extending coherence
This abstract concept has practical consequences for the fragile quantum states. Similar to the well-known Schrödinger’s cat, spins can be simultaneously in a superposition of two or three of the available eigenstates for a certain period, the so-called quantum coherence time.
If the three eigenstates are coupled to each other using the closed contour driving discovered here, the coherence time can be significantly extended, as the researchers were able to show. Compared to systems where only two of the three possible transitions are driven, coherence increased almost a hundredfold.
Such coherence protection is a key element for future quantum technologies and another main result of this work.
Applications for sensor technology
The work described here holds high potential for future applications. It is conceivable that the hybrid resonator-spin system could be used for the precise measurement of time-dependent signals with frequencies in the gigahertz range – for example in quantum sensing or quantum information processing. For time-dependent signals emerging from nanoscale objects, such tasks are currently very difficult to address otherwise. Here the combination of spin and an oscillating system could provide helpful, in particular also because of the demonstrated protection of spin coherence.
Prof. Patrick Maletinsky, University of Basel, Department of Physics, phone +41 61 207 37 63, mail: patrick.maletinsky@unibas.ch
Arne Barfuss, Johannes Kölbl, Lucas Thiel, Jean Teissier, Mark Kasperczyk, and Patrick Maletinsky
Phase-controlled coherent dynamics of a single spin under closed-contour interaction
Nature Physics (2018), doi: 10.1038/s41567-018-0231-8
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unibas.chAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















