New way to write magnetic info could pave the way for hardware neural networks
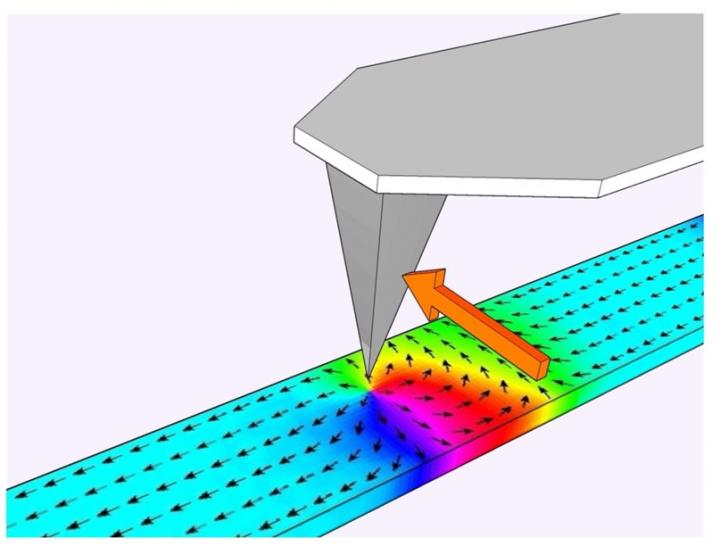
Illustration of the atomic force microscope tip writing a nanowire. Credit: Gartside et al/Imperial College London
Much current computer hardware, such as hard drives, use magnetic memory devices. These rely on magnetic states – the direction microscopic magnets are pointing – to encode and read information.
Exotic magnetic states – such as a point where three south poles meet – represent complex systems. These may act in a similar way to many complex systems found in nature, such as the way our brains process information.
Computing systems that are designed to process information in similar ways to our brains are known as 'neural networks'. There are already powerful software-based neural networks – for example one recently beat the human champion at the game 'Go' – but their efficiency is limited as they run on conventional computer hardware.
Now, researchers from Imperial College London have devised a method for writing magnetic information in any pattern desired, using a very small magnetic probe called a magnetic force microscope. With this new writing method, arrays of magnetic nanowires may be able to function as hardware neural networks – potentially more powerful and efficient than software-based approaches.
The team, from the Departments of Physics and Materials at Imperial, demonstrated their system by writing patterns that have never been seen before. They published their results today in Nature Nanotechnology.
Dr Jack Gartside, first author from the Department of Physics, said: “With this new writing method, we open up research into 'training' these magnetic nanowires to solve useful problems. If successful, this will bring hardware neural networks a step closer to reality.”
As well as applications in computing, the method could be used to study fundamental aspects of complex systems, by creating magnetic states that are far from optimal (such as three south poles together) and seeing how the system responds.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















