Measuring Smallest Magnetic Fields in the Brain Using Diamond and Laser Technology
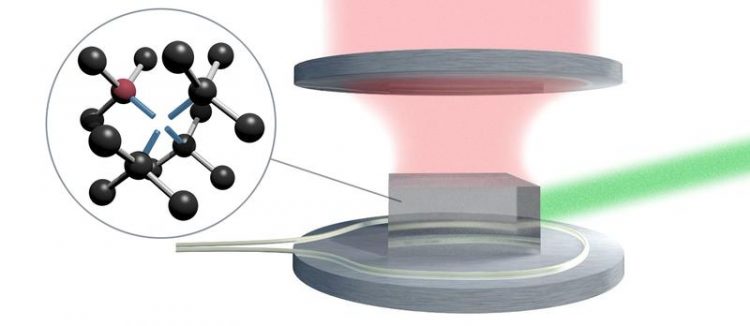
Schematic representation of the laser threshold magnetometry. Insert: An NV center in diamond. © Fraunhofer IAF
The measurement of magnetic fields has become a standard practice in medical diagnostics. Smallest electrical currents flow inside the nerve cells of brains and hearts and produce weak magnetic fields.
Precise magnetic field sensors are able to measure the activity of brains (MEG) or hearts (MKG) and allow for imaging procedures such as magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) in order to detect diseases. The required precision for these measurements, however, is only achieved by a few highly sensitive magnetic field sensors usually working at extreme low-temperature cooling.
Highly Precise Magnetic Field Measurements at Room Temperature
»Most magnetometers are not precise enough to measure the weak signals of the brain. Common highly sensitive magnetic field sensors, such as SQUID sensors, function only with extreme cooling, which makes their use extremely cost-intensive and technologically complex. Innovative sensor technologies such as nitrogen vacancy centers (NV centers) or vapor cell magnetometers could become an important alternative«, explains Dr. Jan Jeske, researcher at Fraunhofer IAF and project manager of »DiLaMag«.
Innovative opportunities for highly sensitive sensor technologies arise from researching new quantum physical systems and from enhancing the materials basis of the sensors. In this regard, the research project »DiLaMag« wants to achieve ultra-sensitive laser threshold magnetometry with the help of atomic nitrogen vacancy centers.
For this purpose, the scientists at Fraunhofer IAF work on the development of the world’s first highly NV-doped diamond laser crystals. Highly sensitive magnetic field sensors, suited for biological applications, would for example allow for the measurement of brain and heart activities of unborn babies, and therefore help prenatal treatment of diseases. The German Ministry for Education and research (BMBF) supports the five-year project as part of their youth competition »NanoMatFutur« – a program to promote young and highly qualified scientists in the field of materials development (FKZ: 13XP5063).
Diamond as a Laser Medium
Laser threshold magnetometry (LSM) is an entirely new research approach. What’s new about it: NV-doped diamond is used as a laser medium in order to develop highly precise laser threshold magnetometers. Jeske developed this concept during his time as a postdoctoral fellow at the RMIT University of Melbourne. »The crucial idea of LSM is based on the concept of using a material as a laser medium that has an optically detectable magnetic resonance.
Diamond with a high density of NV centers is especially well suited as laser medium due to its exceptional material characteristics«, explains Jeske. The scientists expect stronger signals and higher contrasts with NV-doped diamond as laser medium, which will lead to significantly more precise measurement results. »A crucial advantage is the usability of NV centers in diamonds at room temperature, as they maintain their quantum properties – in contrast to, for example, SQUID sensors«, reasons the scientist.
Nitrogen Vacancy Centers in Diamond
Nitrogen vacancy center (NV centers) are atomic systems consisting of one nitrogen atom and a carbon vacancy inside a diamond. They absorb green light and emit red light. As the luminosity of these NV centers depends on the intensity of an exterior magnetic field and as the centers are only the size of an atom, they can be used to measure magnetic fields with both high spatial resolution and high sensitivity.
»The measuring principle is based on the competition between stimulated and spontaneous emission, which can be influenced by smallest magnetic fields«, describes Jeske. The proof that the concept of LSM functions not only theoretically has been provided by first experiments: »The experiments have clearly shown that NV diamond shows stimulated emission and is therefore principally suited as laser material. The next step is to improve the optical properties of diamond and to build the actual measuring system«, says Jeske, who recently returned to the German research scene after his seven-year long stay in Australia.
Setup of a NV Diamond Laser Laboratory
By fusing three core competences of Fraunhofer IAF, namely diamond growth, laser technology and high frequency electronics, quantum magnetometry can quickly be transferred from basics to applied systems. The »DiLaMag« research team now stands at the initial phase of its work: The first step is growing diamonds via a plasma-based CVD procedure and treating them in a way as to minimize losses through absorption, scattering and double scattering. The challenge in this process is to enrich diamond with as many NV centers as possible without lowering the material quality. Subsequently, the project team plans on producing diamond layers with the optimal NV density inside the plasma CVD reactors of Fraunhofer IAF, and to characterize relevant physical and optical parameters of the material. The required infrastructure is currently being established at Fraunhofer IAF.
Project Aims and Cooperation
The aim of the first project stage is to improve the material characteristics of highly NV-doped diamond, as well as its analysis, in order to produce optimized laser crystals and to develop first demonstrators of the LSM. The second project stage focusses on the further improvement of the sensitivity and the measuring of magnetic field signals of biological cells. The project also draws on close cooperation with SIGMA Medizin-Technik GmbH (medical technology Ltd.), who will provide the technical equipment for first biological comparison measurement. The project receives support from the medical side as well, as experts in the field of biomagnetism from the university hospital of Freiburg and Heidelberg will accompany the first measurements.
About Fraunhofer IAF
The Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics IAF ranks among the leading research institutions in the field of compound semiconductors and synthetic diamonds. The Freiburg Institute develops electronic and optoelectronic components, integrated circuits and systems, as well as components on the basis of mono, poly and nanocrystalline diamond.
With its 1000 m² clean room and 3000 m² laboratory space, the Fraunhofer IAF provides equipment for epitaxy, along with measuring techniques, in order to realize high frequency circuits for communication technology, voltage transformer modules for energy technology, infrared and UV detectors for safety technology, infrared laser systems for medical technology, as well as diamond components for innovative applications in the field of quantum sensor technology. Nine microwave plasma reactors are available for diamond synthesization. They allow for the production of ultra-clean diamonds, the growth of diamond layers enriched with isotopes, the performance of delta-doping (N, B, P) and the use of 3D diamond growth.
https://www.iaf.fraunhofer.de/
Originalpublikation:
https://www.iaf.fraunhofer.de/en/media-library/press-releases/DiLaMag.html
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















