Controlling Quantum States Atom by Atom
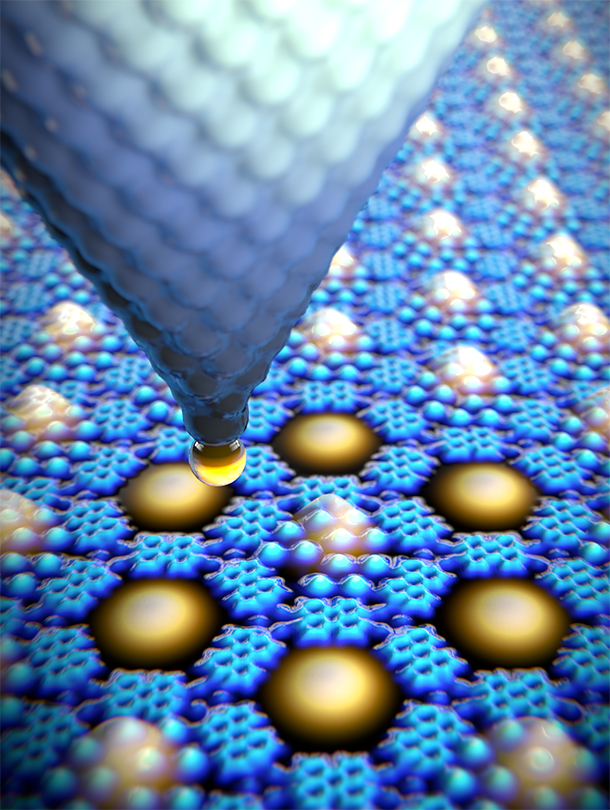
Applications of quantum mechanics are often compromised by the fundamental property of quanta: any measurement inevitably modifies the measured state. Technologies such as quantum computers can be designed only on the basis of known, clearly defined and simple interactions between individual components.
The Department of Physics at the University of Basel together with the Swiss Nanoscience Institute has now developed a method that can be used to study these kinds of interactions in a well-defined system.
Similar to a breadboard in electrical engineering
Breadboards are used in electronic measurement technology to design and test prototypes of electronic circuits and for teaching purposes. The procedure developed by the international consortium led by Prof. Thomas Jung of the University of Basel works in a similar way: for the first time, the new method allows researchers to configure a network of quantum boxes in order to form various quantum electronic states.
A quantum box is an artificially produced structure that restricts a particle’s movements, so that it can move in only two dimensions. This reduces the complexity of a particle interaction and simplifies the process of measurement and analysis.
The research team refined an established method in which atoms are repositioned one after the other using scanning tunneling microscopy, allowing the creation of clearly defined quantum sys-tems. Through the targeted relocating of xenon atoms in quantum boxes, the team succeeded in generating different patterns that correspond to a wide range of quantum states.
Essential tool for quantum technology
The development of quantum technology relies on a detailed understanding of the interdependence between different electronic states; for example, in various atoms. With the physicists’ method, quantum states can be accurately reproduced and interactions between various chemical elements and well-defined electronic states examined – an “unlimited playing field for the study of quantum states”, as the researchers write in Small.
A range of institutions contributed to the project’s success: the theory was outlined by researchers from Linköping (Sweden), the molecules used were synthesized in Heidelberg (Germany), and scientists from San Sebastián (Spain) were responsible for some of the complex measurements of the specific quantum states.
Original article
Sylwia Nowakowska, Aneliia Wäckerlin, Ignacio Piquero-Zulaica, Jan Nowakowski, Shigeki Kawai, Christian Wäckerlin, Manfred Matena, Thomas Nijs, Shadi Fatayer, Olha Popova, Aisha Ahsan, S. Fatameh Mousavi, Toni Ivas, Ernst Meyer, Meike Stöhr, J. Enrique Ortega, Jonas Björk, Lutz H. Gade, Jorge Lobo-Checa, and Thomas A. Jung
Configuring Electronic States in an Atomically Precise Array of Quantum Boxes
Small 2016,00, 1–6 | doi: 10.1002/smll.201600915
Further information
Prof. Thomas A. Jung, University of Basel, Nanolab, tel: +41 56 310 45 18, email: thom-as.jung@psi.ch.
https://www.unibas.ch/en/News-Events/News/Uni-Research/Controlling-Quantum-State…
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















