Causing Collapse
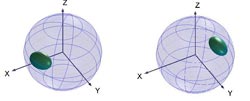
All spin directions (represented by the spheres) collapse on one or the opposite direction depending on the measured photon polarization <br>
One of the most basic laws of quantum mechanics is that a system can be in more than one state – it can exist in multiple realities – at once. This phenomenon, known as the superposition principle, exists only so long as the system is not observed or measured in any way. As soon as such a system is measured, its superposition collapses into a single state. Thus, we, who are constantly observing and measuring, experience the world around us as existing in a single reality.
The principle of superposition was first demonstrated in 1922 by Otto Stern and Walther Gerlach, who observed the phenomenon in the spin of silver atoms. Spin is the intrinsic magnet in quantum particles, and when a particle’s spin is in superposition, it points in more than one direction at the same time. (Instead of the north and south of magnets, these are referred to as up and down.)
Dr. Roee Ozeri and research students Yinnon Glickman, Shlomi Kotler and Nitzan Akerman, of the Physics of Complex Systems Department studied how the spin of a single atom collapsed from superposition to one state when it was observed with light. They “measured” the atom by shining laser light on it. Just as our eyes observe the world by absorbing the photons – light particles – scattered in our direction by objects, the researchers observed the process of spin collapse in the atoms by measuring the scattered photons. In results that appeared recently in Science, they showed that the direction that a photon takes as it leaves the atom is the direction that the spin adopts when superposition collapses.
Next, the team measured the polarization of the emitted photon and found that the observed polarization determines the effect of measurement on the spin. This suggests that an observer can influence the collapse of superposition just by adjusting the orientation of his photon-polarization measurement apparatus.
The reason for this “action-at-a-distance” is that the spins of the measured atoms and the emitted photons were entangled. That is, even after they were separated, a measurement of one of them instantaneously affected the other.
The experiment is an important step in understanding the measurement process in quantum systems.
Dr. Roee Ozeri’s research is supported by the Crown Photonics Center; David Dickstein, France; Martin Kushner Schnur, Mexico; the Wolfson Family Charitable Trust; and the Yeda-Sela Center for Basic Research.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.weizmann.ac.ilAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…





















