Accelerating neutral atoms on a table top
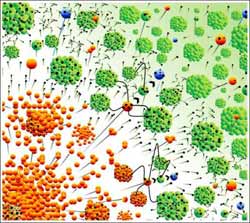
Highly charged Argon ions (orange) exploding from a nanocluster are reduced to neutrals (blue) in a mm accelerator due to dense excited clusters (green).<br><br>Credit: Dr. Rajeev Rajendran, TIFR<br>
In a simple picture, charged particles like electrons and protons are accelerated between two end plates across which an electrical voltage is applied.
High energies need high voltages (millions and billions of volts) and long acceleration paths in giant sized machines – for instance the trillion volt machine called the 'large hadron collider' (LHC) which discovered the Higgs boson, circles over 27 km underground in Geneva! A new concept for a compact accelerator was discovered in the last decade using high powered, short pulses of laser light.
Alternating large electric fields of the light can be transformed in plasmas to create quasi static fields that can produce hundreds of millions volt accelerating voltages just over millimeter lengths on a table top!
How do we accelerate neutral particles- i.e. particles that cannot be energized by electrical voltages? And do it over millimeters rather than hundreds of meters and moreover using lasers? Research at Ultra Short Pulse High Intensity Lab in TIFR has now found a novel scheme that can do precisely this. The concept uses the ability of powerful lasers to strip nearly 8 electrons per atom in a nano sized, cooled aggregate of argon atoms- a nano piece of ice. A 40,000 atom cluster of argon is charged to 320,000 by a laser that lasts only a 100 billionth of a millionth of a second.
Such a super highly charged ice piece explodes soon after, accelerating the charged atoms (Ions) to a million electron volts of energy. The TIFR research now found that all the expelled electrons can be put back into the charged ion that has been accelerated so that it now reverts to being a neutral atom but at high energies. To top it all, this process is nearly 100% efficient at neutralizing the speeding ions and converting them to fast atoms!
Accelerated neutral atoms are very important for many applications. Unaffected by electric or magnetic fields, they penetrate deeper in solids than electrons/ions and thereby create high finesse microstructures for novel electronics and optical devices. Fast atoms are used both as diagnostics and heating sources in Tokomak machines like the ITER (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor) in France, that are being developed to create sustained thermo-nuclear fusion. The TIFR scheme can produce a point source of fast neutral atoms close to the location of an intended application.
As the old adage goes, staying neutral under extreme provocation certainly has its advantages!
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.tifr.res.inAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















