World first self-donning system for surgical gowns
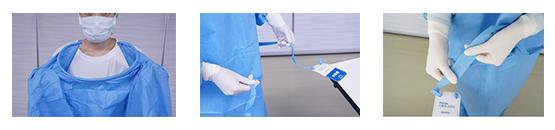
Left to right: This is a special ring around neck, temporary fixing function, tear along perforation. Credit: Osaka University
The research group led by Kiyokazu Nakajima, professor at the Global Center for Medical Engineering and Informatics, Osaka University, has succeeded in developing a safe and easy self-donning and self-adjusting surgical gown called “Selfgown,” which could also minimize environmental infection [1] from splashes when taking off gloves [2].
The group has been working on R&D of medical devices and non-medical equipment [3] to reduce labor burden of medical support staff and to ensure the best use of human resources in order to improve the work environment in health care settings. In this study, the group responded to the strong need to develop a self-donning, self-adjusting surgical gown and succeeded in commercialization after 2 years of R&D.
Conventional surgical gowns are designed to have an assistant tie strings or a belt around the neck, inner gown, and waist to keep arms and hands inside the sterile field. The new gown is comprised of a special spring along the neckline instead of strings.
The inner belt is removed by applying a three-dimensional structure on the rear torso portions to overlap each other. Applying sticky tape on a transfer card for temporary adhesion and forming a special perforation at the end of the waist belt led to the realization of this groundbreaking self-donning, self-adjusting surgical gown.
The notable feature of this gown is that there is practically “zero splashing” of infectious substances from the gloves as the wearer can take off the gown while wrapping the gloves inside-out at the same time, as opposed to a conventional gown where the wearer needs to take off the gloves first in order to undo the strings and the belt.
“We exercised our ingenuity to develop a special ring around the neck and to optimize the structure of rear torso portions to overlap each other,” said Nakajima. “We finally established a self-donning, self-adjusting system after 18 months of research, making 41 prototypes while conducting 17 animal experiments, 5 clinical trials and incorporating evaluations from over 100 surgeons in Japan and overseas. We were able to develop this groundbreaking gown through advice from infection control and critical care specialists. We wish to widely promote our achievement.”
This gown will prevent medical accidents, which are becoming a serious problem, and provide safe and secure medical care. It will also enable medical professionals to initiate immediately at large-scale disasters, emergency areas, and disease outbreaks [4]. Eventually, it may be adapted into nursing care or even use outside of medical care, such as waste disposal or radioactive decontamination work. This gown is now available
###
Glossary:
1: environmental infection: environment (floor, wall or door) contaminated with a virus or bacteria from exposure to splash or contact of body fluids such as blood, vomit or stool.
2: glove: surgical glove
3: non-medical equipment: any surrounding instrument or material to be used for diagnostic, therapeutic or prevention purposes for human beings or animals which are not regulated in the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act, as they are not intended to affect any function of the body of humans or any animals.
4: outbreak: a sudden occurrence of cases of disease in a defined area
Remarks: This research was jointly conducted by Daiei Co., Ltd., Tokusen Industry Co., Ltd. and Osaka University.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…
Innovative microscopy demystifies metabolism of Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Diego have deployed state-of-the art imaging techniques to discover the metabolism driving Alzheimer’s disease; results suggest new treatment strategies. Alzheimer’s disease causes significant problems with memory,…
A cause of immunodeficiency identified
After stroke and heart attack: Every year, between 250,000 and 300,000 people in Germany suffer from a stroke or heart attack. These patients suffer immune disturbances and are very frequently…





















