"Virtual Breast" Could Improve Cancer Detection
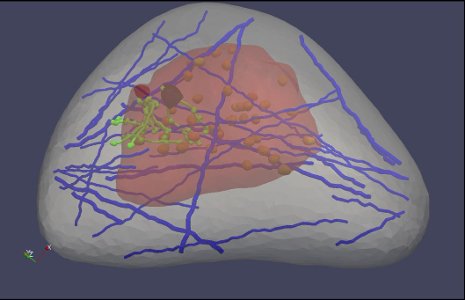
A "virtual breast" image, part of a software program designed by Michigan Tech's Jingfeng Jiang. Healthcare professionals could use the software to learn how to better read ultrasound elastography images, which are used to detect cancer.
That results in lots of needless worry for women and their families—not to mention the time, discomfort and expense of additional tests, including ultrasounds and biopsies.
Recently, a different type of test, ultrasound elastography, has been used to pinpoint possible tumors throughout the body, including in the breast. “It uses imaging to measure the stiffness of tissue, and cancer tissues are stiff,” says Jingfeng Jiang, a biomedical engineer at Michigan Technological University.
Those images can be breathtakingly clear: Jiang shows one elastogram in which the tumor is as different from normal breast tissue as a yolk is from the white in a fried egg. However, not all images are that precise.
“Depending on who does the reading, the accuracy can vary from 95 percent to 40 percent,” he said. “Forty percent is very bad—you get 50 percent when you toss a coin. In part, the problem is that ultrasound elastography is a new modality, and people don’t know much about it.”
Ultrasound elastography could be an excellent screening tool for women who have suspicious mammograms, but only if the results are properly interpreted. Jiang, who helped develop ultrasound elastography when he was a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, reasoned that clinicians might improve their accuracy if they could practice more. So he and his colleagues set about to build a virtual breast.
Like a simulator used to train fledgling surgeons, their virtual breast—a 3D, computer-generated “phantom”—would let medical professionals practice in the safety of the lab. It was developed using data from the Visible Human Project, which gathered thousands of cross-sectional photos from a female cadaver. Thus, it mimics the intricacy of the real thing, incorporating a variety of tissue types and anatomical structures, such as ligaments and milk ducts.
Clinicians can practice looking for cancer by applying virtual ultrasound elastography to the virtual breast and then evaluating the resulting images. Jiang hopes that eventually the lab software will be available to anyone who needs the training.
Jiang’s team, including graduate student Yu Wang and undergraduate Emily Helminen, both of Michigan Tech, presented a poster on their work, “A Virtual Breast Elastography Phantom Lab Using Open Source Software,” at the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, held Sept. 3-6 in Chicago.
Their work is supported by a $452,780 grant from the National Institutes of Health through the National Cancer Institute. The grant number is R15CA179409-01A1.
Michigan Technological University (www.mtu.edu) is a leading public research university developing new technologies and preparing students to create the future for a prosperous and sustainable world. Michigan Tech offers more than 130 undergraduate and graduate degree programs in engineering; forest resources; computing; technology; business; economics; natural, physical and environmental sciences; arts; humanities; and social sciences.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















