The strange double life of Dab2
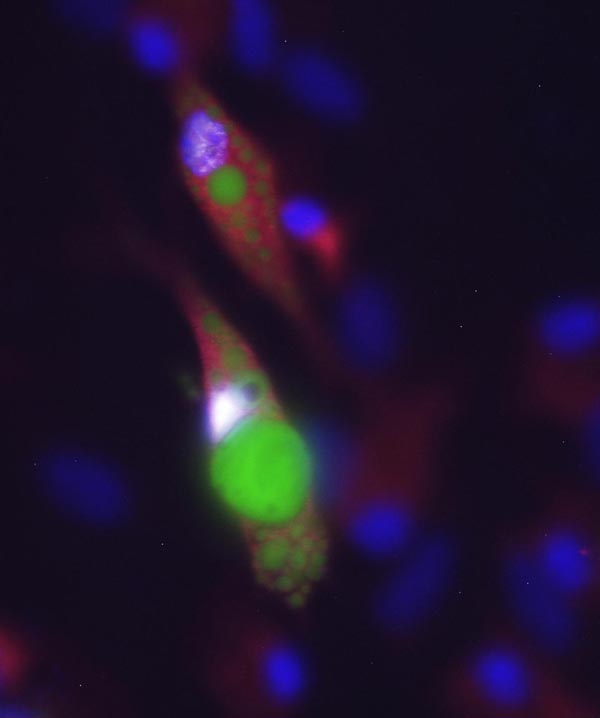
These are Dab2 (red)-positive pre-adipocytes accumulating lipid droplets (green). Credit: Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center
Sometimes proteins do a lot more than we expect. Dab2, for example, has long been linked to cancer. The molecule is associated with a chain of signaling proteins called the Ras-MAPK pathway. In many cancers, elements of Ras-MAPK mutate and start telling cells to grow uncontrollably.
Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center researcher Xiang-Xi Michael Xu, Ph.D., who is also a professor of cell biology at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, discovered Dab2 more than 20 years ago and has been studying its relationship to cancer ever since. But now he's found that Dab2 has been living a secret life all along – one that could have public health implications for fighting obesity. In a paper published in the journal Scientific Reports, the Xu lab has shown that young mice without Dab2 don't gain weight when given excessive food.
“These mice look and act normal,” says Xu. “Everything seems fine, except when we give them a high-fat diet. They just don't get fat.”
The underlying mechanism may revolve around fat stem cells: immature cells that can either divide into more stem cells or differentiate into mature fat cells. In normal mice, Dab2 suppresses Ras-MAPK, which in turn elevates a protein called PPAR, which helps fat stem cells make the jump to mature fat cells. Eliminating Dab2 short-circuits that process.
While normal mice eating a calorie-dense diet pack on weight, the Dab2 knockouts stay lean – but only for a while. As the mice mature, the metabolic effect dissipates. By six months, the loss of Dab2 has virtually no effect.
Xu believes this happens because mice (and humans) lose their fat stem cells as they reach maturity. This early impact could help explain why early weight problems could persist into adulthood and many adults have such a hard time losing weight.
“Dab2 controls a population of fat stem cells that slowly disappears,” said Xu. “It seems that children are especially affected by diet. They can both increase fat cell number and fat cell size when they are young. Later in life, they can still make fat, but that's existing fat cells getting bigger. Habits of childhood could be affecting adults, making them more susceptible to obesity.”
From a public health standpoint, these findings may reinforce the importance of steering children away from high-fat diets. Identifying this role for Dab2 could also lead to new pharmaceutical strategies to combat childhood obesity, as the protein could make an attractive target for drug development.
“It would be very hard for a small laboratory like ours to develop a new drug that targets Dab2,” said Xu. “But perhaps a pharmaceutical company will pick it up and develop it.”
###
About Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center
Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of UHealth – the University of Miami Health System and the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, is among the nation's leading cancer centers and South Florida's only Cancer Center of Excellence. A 2015 study by Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, published in The Journal of the American Medical Association, showed that cancer patients treated at Sylvester have a 10 percent higher chance of survival than those treated at nearly any other cancer center in the nation.
With the combined strength of more than 120 cancer researchers and 130 cancer specialists, Sylvester discovers, develops and delivers more targeted therapies, providing the next generation of cancer clinical care – precision cancer medicine – to each patient. Our comprehensive diagnostics, coupled with teams of scientific and clinical experts who specialize in just one type of cancer, enable us to better understand each patient's individual cancer and develop treatments that target the cells and genes driving the cancer's growth and survival, leading to better outcomes.
At Sylvester, patients have access to more treatment options and more cancer clinical trials than most hospitals in the southeastern United States. To better serve current and future patients, Sylvester has a network of conveniently located outpatient treatment facilities in Miami, Kendall, Hollywood, Plantation, Deerfield Beach, Coral Springs, and Coral Gables. For more information, visit sylvester.org.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles
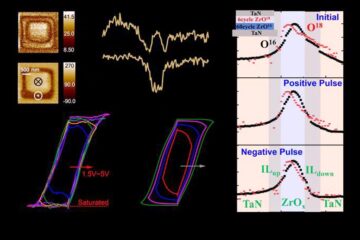
Evidence for reversible oxygen ion movement during electrical pulsing
…enabler of the emerging ferroelectricity in binary oxides. In a recent study published in Materials Futures, researchers have uncovered a pivotal mechanism driving the emergence of ferroelectricity in binary oxides….
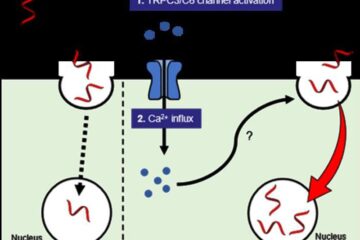
Next-generation treatments hitch a ride into cancer cells
Researchers from Osaka University discover that opening a channel into cancer cells helps antisense oligonucleotide drugs reach their targets. Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) are next-generation drugs that can treat disease by…

Boron deficiency: oilseed rape reacts as with infection and pest infestation
Genetic mechanisms uncovered… Boron deficiency has a devastating effect on oilseed rape and related plants. However, little is known about the underlying genetic mechanisms. A study shows that the response…





















