Successful outcome of Voluntary Harmonisation Procedure for clinical trials in Germany
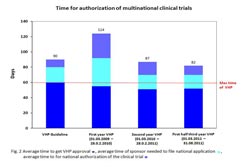
Time for authorisation of multinational clinical trials - changes after start of VHP. Photo: Paul-Ehrlich-Institut<br>
The situation was reviewed after three years and showed a positive outcome: The time that elapses before a multinational clinical trial is authorised in all participating EU countries could be reduced to less than three months. Reports on previous experience and further steps planned by experts of the PEI can be found in the online edition of Nature Reviews Drug Discovery of 10 April 2012 (doi:10.1038/nrd3202-c2)
The development of new and innovative medicinal products is a long and tedious process. After the preclinical phase of development, potential medicinal products have to be tested for their safety and efficacy in a number of clinical trials. In each European country where a clinical trial is planned to be performed, such a clinical trial requires a national authorisation.
If a clinical trial was to be performed in more than one European country, this meant for a long time that it had to undergo the entire procedure of validation, assessment, grounds for non-acceptance/reply, and authorisation/rejection right from the start. In the case of multinational trials with more than ten member states, it could easily take more than one year before the authorisation was obtained in all countries.
The 'Clinical Trials Facilitation Group' (CTFG), a working group of the HMA ('Heads of Medicines Agencies'), decided to remedy the situation. With the experts of the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut (PEI) being in charge, the group developed a procedure which presents a major progress both for the applicants and for the medicines agencies in Europe: The 'Voluntary Harmonisation Procedure‘ (VHP). Since March 2009 the CTFG has offered applicants who intend to perform a clinical trial in three or more EU member states the opportunity to start a single authorisation procedure in these countries.
“The verification and evaluation of clinical trials is of central importance for the development of new medicinal products. To harmonise these procedures in Europe, thus assuring a more rapid and at the same time more thorough evaluation, is a major concern for us at the PEI. I am very happy that the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut assumed a leading role in this process”, said Professor Klaus Cichutek, the president of the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut.
A current evaluation shows that the procedure has in fact clearly accelerated the authorisation of multinational clinical studies: In 2011, the average period required until the authorisation of a multinational clinical trial was obtained amounted to only 82 day. Previously, it took up to several months or even one year. The actual harmonisation procedure, on the other hand takes only 50 days on average. Applicants are required to apply for an authorisation in the individual countries in which the study is to be conducted within 20 days following a favourable opinion. The deadline for such cases is now only ten days, which is feasible since all scientific questions have already been answered in the new harmonised procedure. The time period required for obtaining an authorisation of multinational clinical trials could be reduced from 124 days in the first year to currently 82 days within three years thanks to the fact that the harmonisation procedure has already undergone several revisions.– an advantage of this voluntary procedure, which requires no change in the law, and in which useful changes can be implemented on a short-term basis.
“The procedure is an important simplification for applicants and medicines agencies that assess the medicinal products. The procedures themselves are accelerated, resources of the parties involved are used in an optimum manner, and are not overburdened by double work” explained Dr Hartmut Krafft, chairman of the CTFG. This statement made in his role as an expert should be correct, since experts of the PEI coordinate all harmonisation procedures, regardless of whether the clinical trials are performed in Germany or not.
The number of applications is on the increase: In 2009, 26 applications were made. In 2011, this figure was 85, and the number is increasing further. Altogether, 170 applications have been made so far. Whereas after the introduction of VHP, the procedure was at first used by university institutions and small businesses, it is now also appreciated by large pharmaceutical companies – including companies outside Europe: More than 40% of the applications with office in the USA.
The European Commission, too, deems it necessary to harmonise the procedures. For mid-2012, a draft for a new Directive on clinical trials is expected.
Original publication:
Krafft H, Bélorgey C, Szalay G.: Experience and further development with the Voluntary Harmonization Procedure for multinational clinical trials in the European Union. 2012, doi:10.1038/nrd3202-c2
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

“Nanostitches” enable lighter and tougher composite materials
In research that may lead to next-generation airplanes and spacecraft, MIT engineers used carbon nanotubes to prevent cracking in multilayered composites. To save on fuel and reduce aircraft emissions, engineers…

Trash to treasure
Researchers turn metal waste into catalyst for hydrogen. Scientists have found a way to transform metal waste into a highly efficient catalyst to make hydrogen from water, a discovery that…

Real-time detection of infectious disease viruses
… by searching for molecular fingerprinting. A research team consisting of Professor Kyoung-Duck Park and Taeyoung Moon and Huitae Joo, PhD candidates, from the Department of Physics at Pohang University…





















