Controlling neglected tropical diseases could help make poverty history
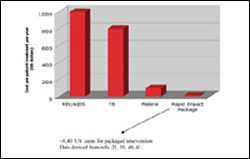
Caption: Range of Treatment Costs Per Year for Treating HIV/AIDS, TB, Malaria, and Neglected Tropical Diseases (Rapid Impact Package)
“The big three” infections AIDS, TB and malaria have caught the world’s attention but other disabling and fatal infectious diseases in Africa are being ignored, say three eminent tropical disease researchers in the international health journal PLoS Medicine.
The neglected tropical diseases, which include sleeping sickness, schistosomiasis, river blindness, hookworm, elephantiasis, and blinding trachoma, affect several hundred million people, and kill at least half a million annually, and yet they garner little attention from donors, policymakers, and public health officials.
The researchers, led by Professor David Molyneux, Director of the Lymphatic Filariasis Support Centre at the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, argue that a “rapid impact package””Xdistribution of four anti-parasitic drugs across Africa to treat seven neglected diseases”Xwould bring tangible benefits to the world”’s poorest communities.
The cost of the package, they say, would be negligible”Xa mere 40 cents per person per year, compared with a minimum of $200 per person per year to treat HIV/AIDS, $200 to treat a single episode of TB, and $7-10 to treat a single episode of malaria.
Three of the drugs in the package (ivermectin, azithromycin, and albendazole) are being donated by their manufacturers, and the fourth (praziquantel) now costs only 7 cents per tablet.
Professor Molyneux and his colleagues, Professor Peter Hotez of the Human Hookworm Initiative and Professor Alan Fenwick of the Schistosomiasis Control Initiative, argue that a rapid impact package against some of the neglected tropical diseases could permanently reduce their incidence.
For costs that are relatively modest compared to controlling “the big three,”an integrated control package for neglected tropical diseases could have a proportionately greater impact on more poor people’s health as well as being more equitable for the majority of Africa’s poorest and marginalised communities.
The researchers “urge policy makers and health economists to recognize that although HIV, TB, and malaria are the most serious problems facing health planners, other diseases exist that can be addressed at realistic costs with effective interventions.”
“Controlling Africa”’s neglected diseases is one of the more convincing ways to “make poverty history” through affordable, pro-poor, effective, and tested strategies.”
Citation: Molyneux DH, Hotez PJ, Fenwick A (2005) “Rapid-impact interventions”: How a policy of integrated control for Africa”’s neglected tropical diseases could benefit the poor. PLoS Med 2(11): e336.
An embargoed press briefing will be taking place at the Science Media Centre (SMC), 21 Albemarle St, London at 11am Monday 10th October. If you would like to attend, please call Becky Morelle on 0207-670-2932. Please note the SMC has no dial-in facilities.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.plos.orgAll latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















