Nanoparticles offer new hope for detection and treatment
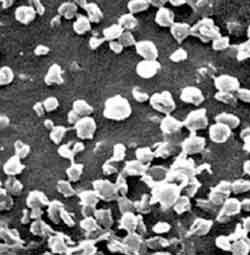
The nanoparticles shown here are irregularly shaped due to the fixing process for electron microscopes. They are normally perfect spheres.
Particles could make earlier cancer diagnosis possible
Specially designed nanoparticles can reveal tiny cancerous tumors that are invisible by ordinary means of detection, according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
The researchers demonstrated that very small human melanoma tumors growing in mice—indiscernible from the surrounding tissue by direct MRI scan—could be “lit up” and easily located as soon as 30 minutes after the mice were injected with the nanoparticles.
Because nanoparticles can be engineered to carry a variety of substances, they also may be able to deliver cancer-fighting drugs to malignant tumors as effectively as they carry the imaging materials that spotlight cancerous growth. “One of the best advantages of the particles is that we designed them to detect tumors using the same MRI equipment that is in standard use for heart or brain scans,” says senior author Gregory Lanza, M.D., Ph.D., associate professor of medicine. “We believe the technology is very close to being useful in a hospital setting.”
Lanza and his colleague Samuel Wickline, M.D., professor of medicine, are co-inventors of this nanoparticle technology. The effectiveness of the nanoparticles in diagnosis and therapy in humans will be tested in clinical trials in about one and a half to two years. The spherical nanoparticles are a few thousand times smaller than the dot above this “i,” yet each can carry about 100,000 molecules of the metal used to provide contrast in MRI images. This creates a high density of contrast agent, and when the particles bind to a specific area, that site glows brightly in MRI scans.
In this study, MRI scans picked up tumors that were only a couple of millimeters (about one twenty-fifth of an inch) wide. Small, rapidly growing tumors cause growth of new blood vessels, which feed the tumors. To get the particles to bind to tumors, the researchers equipped them with tiny “hooks” that link only to complementary “loops” found on cells in newly forming blood vessels. When the nanoparticles hooked the “loops” on the new vessels’ cells, they revealed the location of the tumors. Nanoparticles are particularly useful because of their adaptability, according to Lanza, who sees patients at Barnes Jewish Hospital. “We can also make these particles so that they can be seen with nuclear imaging, CT scanning and ultrasound imaging,” Lanza says.
In addition, the particles can be loaded with a wide variety of drugs that will then be directed to growing tumors. “When drug-bearing nanoparticles also contain an imaging agent, you can get a visible signal that allows you to measure how much medication got to the tumor,” Lanza says. “You would know the same day you treated the patient and if the drug was at a therapeutic level.” Using nanoparticles, drug doses could be much smaller than doses typically used in chemotherapy, making the procedure potentially much safer. “The other side of that is you have the ability to focus more drug at the tumor site, so the dose at the site might be ten to a thousand times higher than if you had administered the drug systemically,” Lanza says.
The nanoparticles also may permit more effective follow up, because a doctor could use them to discern whether a tumor was still growing after radiation or chemotherapy treatments. Although this study focused on melanoma tumors, the researchers believe the technology should work for most solid tumors, because all tumors must recruit new blood vessels to obtain nutrients as they grow. Nevertheless, melanoma has unique traits that make it especially interesting as a target for nanoparticle therapy. Melanoma has a horizontal phase, when it spreads across the skin surface, and a vertical phase, when it goes deep into the body and grows quickly. “Once melanoma has moved into its vertical phase, it is almost untreatable because by the time the tumors are large enough to detect, it’s too late,” Lanza says. “With the nanoparticles, we believe we would be able to see the smallest melanoma tumors when they are just large enough to begin new blood vessel formation. Plus, we should be able to deliver chemotherapeutic drugs right to melanoma cells, because melanoma tumors create blood vessels using their own cells.”
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.wustl.eduAll latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















