New technique could prevent dangerous biofilms on catheters
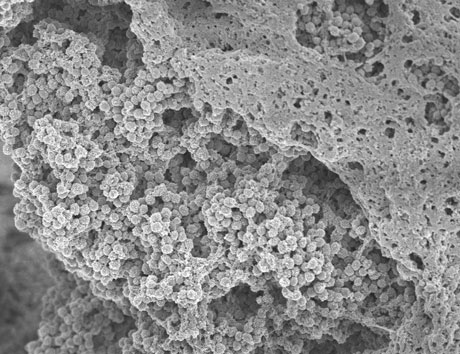
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria forming biofilm - New technique could prevent dangerous biofilms on catheters University of Gothenburg
Biofilms are mats of bacteria similar to the plaque that grows on teeth. Biofilms frequently coat the surfaces of catheters, and of various medical implants and prostheses, where they can threaten lives or lead to failure of the implants.
Antibiotics are impotent against biofilms. Now Gothenburg researchers Jakub Kwiecinski, Tao Jin and collaborators show that coating implants with “tissue plasminogen activator” can prevent Staphylococcus aureus, the leading cause of hospital-acquired infections, from forming biofilms.
Hijacks the system
A growing biofilm requires anchoring, and in earlier research, this team, led by Jin, an Associate Professor of Rheumatology and Inflammation Research, the University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden, had discovered that S. aureus hijacks the human clotting system to create a scaffold of micro-clots to support the growing biofilm.
“We hypothesized that if we forced the human body to start dissolving those clots, we could prevent the biofilm from developing,” said Kwiecinski, a post-doctoral researcher in Jin’s laboratory.
Clot-dissolving protein
To encouraging the clot-busting, the investigators coated the surfaces with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), which activates the clot-dissolving protein, plasminogen.
“This deprives S. aureus of a scaffold for biofilm formation and prevents infection,” said Kwiecinski. After performing the research under laboratory conditions, they confirmed that it works by coating catheters that they then implanted into laboratory mice.
Looking beyond bacteria
A key to the team’s success was their decision to look beyond the bacteria, the stopping place for most previous research, to the human body’s involvement in the infections, said Kwiecinski. The clot-busting, he said, could be applied to biofilms of pathogens other than S. aureus.
Biofilm-related infections afflict around 1.7 million in the US alone, killing nearly 100,000 annually, according to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention. “With increasing numbers of prosthetic devices used in modern medicine, this number is only going to increase,” said Kwiecinski. Thus, the research could lead to a major reduction in hospital-acquired disease and death.
The article Tissue plasminogen activator coating on implant surfaces reduces Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation was published online in Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
Link to article: http://aem.asm.org/cgi/reprint/AEM.02803-15v1?ijkey=jEqeGWGNE/hZk&keytype=re…
For more information please contact:
Tao Jin, Associate Professor at the Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg
+4631-3429710
tao.jin@rheuma.gu.se
Jakub Kwiecinski, postdoc at The University of Iowa, USA, former PhD-student at the Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg
jakub.kwiecinski@rheuma.gu.se
http://sahlgrenska.gu.se/english/research/news-article/?languageId=100001&co…
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

“Nanostitches” enable lighter and tougher composite materials
In research that may lead to next-generation airplanes and spacecraft, MIT engineers used carbon nanotubes to prevent cracking in multilayered composites. To save on fuel and reduce aircraft emissions, engineers…

Trash to treasure
Researchers turn metal waste into catalyst for hydrogen. Scientists have found a way to transform metal waste into a highly efficient catalyst to make hydrogen from water, a discovery that…

Real-time detection of infectious disease viruses
… by searching for molecular fingerprinting. A research team consisting of Professor Kyoung-Duck Park and Taeyoung Moon and Huitae Joo, PhD candidates, from the Department of Physics at Pohang University…





















