Bioinspired nanoscale drug delivery method developed by WSU, PNNL researchers
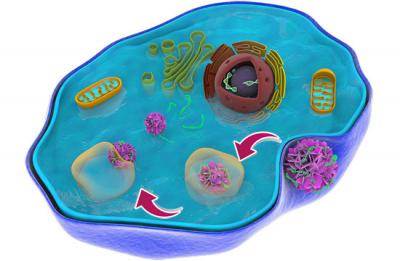
Schematic representation of the movement of the flower-like particle as it makes its way through a cellular trap to deliver therapeutic genes. Credit: WSU
The work could someday lead to more effective therapies and diagnostics for cancer and other illnesses.
Led by Yuehe Lin, professor in WSU's School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, and Chunlong Chen, senior scientist at the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL), the research team developed biologically inspired materials at the nanoscale that were able to effectively deliver model therapeutic genes into tumor cells. They published their results in the journal, Small.
Researchers have been working to develop nanomaterials that can effectively carry therapeutic genes directly into the cells for the treatment of diseases such as cancer.
The key issues for gene delivery using nanomaterials are their low delivery efficiency of medicine and potential toxicity.
“To develop nanotechnology for medical purposes, the first thing to consider is toxicity — That is the first concern for doctors,” said Lin.
The flower-like particle the WSU and PNNL team developed is about 150 nanometers in size, or about one thousand times smaller than the width of a piece of paper.
It is made of sheets of peptoids, which are similar to natural peptides that make up proteins. The peptoids make for a good drug delivery particle because they're fairly easy to synthesize and, because they're similar to natural biological materials, work well in biological systems.
The researchers added fluorescent probes in their peptoid nanoflowers, so they could trace them as they made their way through cells, and they added the element fluorine, which helped the nanoflowers more easily escape from tricky cellular traps that often impede drug delivery.
The flower-like particles loaded with therapeutic genes were able to make their way smoothly out of the predicted cellular trap, enter the heart of the cell, and release their drug there.
“The nanoflowers successfully and rapidly escaped (the cell trap) and exhibited minimal cytotoxicity,” said Lin.
After their initial testing with model drug molecules, the researchers hope to conduct further studies using real medicines.
“This paves a new way for us to develop nanocargoes that can efficiently deliver drug molecules into the cell and offers new opportunities for targeted gene therapies,” he said.
The WSU and PNNL team have filed a patent application for the new technology, and they are seeking industrial partners for further development.
###
The work was funded by Washington State University start-up funds and the Department of Energy.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















