A specific protein regulates the burning of body fat to generate heat
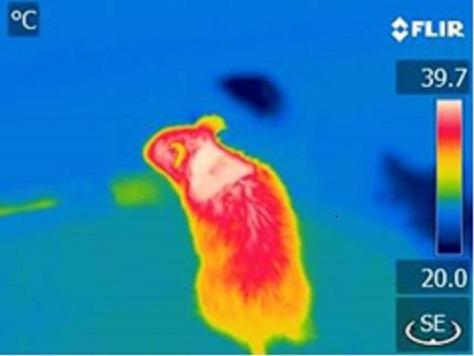
This is a thermal image of a mouse, with white indicating the location of brown fat (maximum heat generation). Photo: Nuria Matesanz, CNIC
Scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares Carlos III (CNIC) have identified a protein that holds promise as a target for therapies to reduce obesity. Drs. Guadalupe Sabio and Nuria Matesanz have demonstrated that MKK6 controls the conversion of fat stores, known as white fat, into brown fat, in which lipids are burned to maintain body temperature and reduce obesity. The study is published today in Nature Communications.
Obesity is a global epidemic, with overweight or obesity affecting an estimated 2200 million people worldwide. The research team led by Guadalupe Sabio analyzed fat tissue samples from obese patients at the University Hospital in Salamanca, and found that these samples contained above-normal levels of the protein MKK6. Detailed analysis of MKK6 function showed that this protein impedes the conversion of fat stores, known as white fat, into brown fat, in which lipids are burned to maintain body temperature.
Brown fat has attracted a lot of interest in recent years among obesity researchers. Body fat is essential for maintaining an appropriate energy balance and regulating body temperature. But not all fat is the same. The body contains two types of fat tissue: white adipose tissue is a store of excess calories, whereas brown adipose tissue is considered a 'good' fat that burns lipids to maintain body temperature.
Brown fat can be activated by cold to “generate heat instead of storing fat,” explained Sabio. But the most interesting observation is that “white adipose tissue can be converted into brown adipose tissue, thus increasing body temperature.”
According to Dr. Sabio, this has led to a burgeoning interest in the clinical potential of brown fat, since “activation of this tissue could reduce excess weight.” According to Nuria Matesanz, the results of the study indicate that obese individuals lose the ability to activate brown fat or to convert white fat in to brown, and therefore are unable to lose weight via this route.
In addition to the participation of partners at the the University Hospital in Salamanca, the Nature Communications study was conducted in collaboration with the research group led by Dr. José Antonio Enríquez at the CNIC and research teams from the Universidad de Extremadura and the Centro de Investigación en Medicina Molecular y Enfermedades Crónicas (CiMUS) in Santiago de Compostela.
The researchers found that the inability to convert white fat to brown in obese patients is caused by increased amounts of the protein kinase MKK6. Through the use of animal models, the research team was able to demonstrate that MKK6 prevents the conversion white fat into brown. Mice lacking MKK6 have more brown fat; consequently, these mice are protected against obesity and eliminate excess energy as heat.
The research also demonstrated that eliminating MKK6 after mice had become obese stopped the further development of obesity and led to a drop in body weight. These findings all point to the potential of MKK6 as a therapeutic target in the fight against obesity.
###
About the CNIC
The Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC), directed by Dr. Valentín Fuster, is dedicated to cardiovascular research and the translation of knowledge gained into real benefits for patients. The CNIC, recognized by the Spanish government as a Severo Ochoa center of excellence, is financed through a pioneering public-private partnership between the government (through the Carlos III Institute of Health) and the Pro-CNIC Foundation, which brings together 14 of the most important Spanish private companies.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















