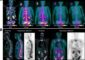
The first research facility in Poland to be equipped with a 3T magnetic resonance scanner
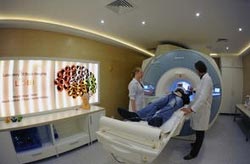
Examination using a nuclear magnetic scanner in the Laboratory of Brain Imaging of the Neurobiology Center in the Nencki Institute, Warsaw, Poland. (Source: Nencki Institute, Grzegorz Krzy¿ewski) <br>
Such a device has been put in operation in the newly opened Laboratory of Brain Imaging. For the first time in Poland a diagnostic device of such class will be employed solely in the service of science.
There are over a hundred medical MRI scanners in Poland. When installed in hospitals, they are used as indispensable non-invasive devices for diagnosing internal organs with patients’ exams being the top priority. As a result, the availability of MRI scanners for Polish scientists was limited, which restricted the possibilities of conducting advanced research of the brain structure (sMRI) and function (fMRI). As of today these problems belong to the past. The Laboratory of Brain Imaging, which opened in the Neurobiology Center of the Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology in Warsaw, is equipped with a 3 Tesla magnetic resonance scanner dedicated exclusively to scientific research.
This new lab of the Nencki Institute was built and equipped from European funds under the Warsaw Centre for Preclinical Research and Technology (CePT) and it is a core facility. This means that the equipment assembled in the lab can be used by all interested researchers. “Our task is not limited to making the device available and servicing it. We also help develop projects and select appropriate research methods for them”, emphasize people working at the lab. Even though the lab has just opened, its research schedule is already full for the whole next year.
This up-to-date MRI scanner allows Polish scientists from research centres and universities to carry out advance structural and functional imaging of the human brain. A new program is already underway of examining children with developmental dyslexia. It aims at developing better methods for diagnosing the disorder and developing more effective ways of selecting therapeutic methods. A special dummy of the MRI scanner has been built for the project to make children familiar with the experimental procedure. This project, executed in the Laboratory of Brain Imaging, is carried out by an interdisciplinary research team from the Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology and the Warsaw University of Technology. Other projects executed in the lab are funded by the NCN or NCBiR and are conducted by Prof. Ma³gorzata Kossut, Prof. Andrzej Wróbel and Prof. El¿bieta Szel¹g.
In addition the Laboratory of Brain Imaging is involved in the execution of numerous other projects by cooperating scientists from the Medical University of Warsaw, University of Warsaw, Jagiellonian University, Adam Mickiewicz University, University of Physical Education in Wroc³aw and the University of Social Sciences and Humanities. The scope of this research reflects a wide spectrum of processes, among other brain and language plasticity, anxiety disorders, disorders of long term memory, empathy and genetics of behaviour.
The MRI scanner will also find application in research on Alzheimer’s disease. Of critical importance in case of this disease is early detection of neurodegenerative changes occurring in the brain. Unfortunately, the clinical symptoms related to Alzheimer’s disease appear already a few years after the first changes take place when it is already too late to start treatment. At the present time medical science does not have a remedy for Alzheimer’s disease, but it is expected it to be available sooner or later. Then detection of the neurodegenerative changes within the brain as early as possible will be of primary importance.
Currently apart from the MRI scanner, the Laboratory of Brain Imaging is equipped with newly purchased state-of-the-art device for electroencephalographic research (EEG) and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). The EEG device makes it possible to register changes in the electric activity of the brain with high time accuracy measured in milliseconds. Currently conducted research involves using a method of simultaneous EEG-fMRI registration and is carried out in cooperation with the Faculty of Psychology of the University of Warsaw. Using simultaneous registration, the scientists wish to understand brain mechanisms related to fear perception. The TMS device, on the other hand, can be used to stimulate or inhibit selected brain centres with the help of local magnetic field. These additional devices create a specialized and unique in Poland workstation for researching the human brain.
The Laboratory of Brain Imaging is one of the labs set up in the Neurobiology Center, which is a new structure within the Nencki Institute established under a European project entitled Centre for Preclinical Research and Technology CePT. With the budget of over 388 million PLN, CePT is the largest biomedical and biotechnological undertaking in Central and Eastern Europe. Under the CePT project, of which Nencki Institute is one of several participants, a network of interconnected core facilities is being established within the Warsaw Ochota campus, integrating scientific and implementation activities of many research institutions. These labs are equipped to carry out basic and preclinical research at the highest European level in the area of protein structural and functional analysis, physical chemistry and nanotechnology of biomaterials, molecular biotechnology, aiding medical technologies, pathophysiology and physiology, oncology, genomics, neurobiology and ageing related diseases.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://press.nencki.gov.plAll latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…