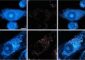
New 3D light microscopy method reveals new perspectives on the dynamics of the cell’s skeleton

The technological advance, which is published in the current online issue of Nature Methods, allows for the first time the observation of the intrinsic dynamic properties of microtubules. These constitute a major part of the cell’s skeleton and can now be observed in a mechanically unconstrained and at the same time physiologically relevant context.
Microtubules form a network of protein filaments, which constantly grow and shrink. This network’s behaviour is controlled by the intrinsic properties of many different proteins. Conventional microscopy studies microtubules and other filaments in artificial set-ups, which biases certain behaviour and introduces artefacts via the hard and flat surfaces of the surrounding glass chamber.
Ernst Stelzer and his colleagues Philipp Keller and Francesco Pampaloni at EMBL have managed to overcome the limitations of traditional microscopy and discovered different microtubule behaviour in an unrestricted environment, resulting in a highly accurate characterisation of intrinsic microtubule dynamics in a close to life context.
The new method is currently being adopted to study other dynamic cellular processes. The authors expect their results to have a major impact on the understanding of the mechanical properties of tissue cells. This will also influence current nanobiotechnology and have a significant effect on cancer research.
Published online in Nature Methods on 10 September 2007.
http://www.embl.org/aboutus/news/press/2007/10sept07/
Lena Raditsch
Head of Communications
Office of Information and Public Affairs
EMBL
Meyerhofstr. 1
69117 Heidelberg
Germany
T: +49 6221 387 8125
F: +49 6221 387 8525
M:+49 151 14532784
lena.raditsch@embl.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…