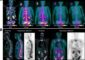
New imaging technique can identify breast cancer subtypes and early treatment response

“The process of targeted drug development requires assays that measure drug target engagement and predict the response (or lack thereof) to treatment,” said Alex Walsh, a graduate student in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn.
“We have shown that optical metabolic imaging (OMI) enables fast, sensitive, and accurate measurement of drug action. Importantly, OMI measurements can be made repeatedly over time in a live animal, which significantly reduces the cost of these preclinical studies.”
Human cells undergo extensive chemical reactions called metabolic activity to produce energy, and this activity is altered in cancer cells. When cancer cells are treated with anticancer drugs, their metabolic activity changes. OMI takes advantage of the fact that two molecules involved in cellular metabolism, called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), naturally emit fluorescence when exposed to certain forms of light. In this way, OMI generates distinct signatures for cancer cells with a different metabolism and their responses to drugs.
Walsh and colleagues used a custom-built, multiphoton microscope and coupled it with a titanium-sapphire laser that causes NADH and FAD to emit fluorescence. They used specific filters to isolate the fluorescence emitted by these two molecules, and measured the ratio of the two as “redox ratio.”
When they placed normal and cancerous breast cells under the microscope, OMI generated distinct signals for the two types of cells. OMI could also differentiate between estrogen receptor-positive, estrogen receptor-negative, HER2-positive, and HER2-negative breast cancer cells.
Next, the researchers tested the effect of the anti-HER2 antibody trastuzumab on three breast cancer cell lines that respond differently to the antibody. They found that the redox ratios were significantly reduced in drug-sensitive cells after trastuzumab treatment but unaffected in the resistant cells.
They then grew human breast tumors in mice and treated some of these with trastuzumab. When they imaged tumors in live mice, OMI showed a difference in response between trastuzumab-sensitive and -resistant tumors as early as two days after the first dose of the antibody. In comparison, FDG-PET imaging, the standard clinical metabolic imaging technique, could not measure any difference in response between trastuzumab-sensitive and -resistant tumors at any time point in the experiment, which lasted 12 days.
“Cancer drugs have profound effects on cellular energy production, and this can be harnessed by OMI to identify responding cells from nonresponding cells,” said Walsh. “We are hoping to develop a high-throughput screening method to predict the optimal drug treatment for a particular patient.”
Importantly, OMI can be used on tissues freshly excised from patients but, with further development, it could be incorporated in endoscopes for live imaging of human cancers, according to the investigators.
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, the Department of Defense Breast Cancer Research Program, Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center, and Vanderbilt University Medical Center. The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Follow the AACR on Twitter: @AACR
Follow the AACR on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/aacr.org
About the American Association for Cancer Research
Founded in 1907, the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) is the world's oldest and largest professional organization dedicated to advancing cancer research and its mission to prevent and cure cancer. AACR membership includes more than 34,000 laboratory, translational, and clinical researchers; population scientists; other health care professionals; and cancer advocates residing in more than 90 countries. The AACR marshals the full spectrum of expertise of the cancer community to accelerate progress in the prevention, biology, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer by annually convening more than 20 conferences and educational workshops, the largest of which is the AACR Annual Meeting with more than 18,000 attendees. In addition, the AACR publishes eight peer-reviewed scientific journals and a magazine for cancer survivors, patients, and their caregivers. The AACR funds meritorious research directly as well as in cooperation with numerous cancer organizations. As the scientific partner of Stand Up To Cancer, the AACR provides expert peer review, grants administration, and scientific oversight of team science and individual grants in cancer research that have the potential for near-term patient benefit. The AACR actively communicates with legislators and policymakers about the value of cancer research and related biomedical science in saving lives from cancer. For more information about the AACR, visit http://www.AACR.org.
To interview Alex Walsh, contact Dagny McMillin at 615-936-7245 or dagny.stuart@vanderbilt.edu. For other inquiries, contact Jeremy Moore at jeremy.moore@aacr.org or 215-446-7109.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.aacr.orgAll latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…