A technology to transform 2D planes into 3D soft and flexible structures
This is the cover image of the ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces publishing the research paper. Credit: DGIST
DGIST announced that Professor Sohee Kim's research team in the Department of Robotics Engineering succeeded in developing a technology to produce flexible 3D medical devices. It is expected to be used in developing various devices with embedded electrical functionality or soft robots.
Professor Sohee Kim's team developed a new technology for 3D device production that selectively bonds polymeric thin films using plasma. Since this technology can manufacture 3D flexible devices more easily than the existing methods, it is expected to have a positive impact on the future research.
The existing flexible 3D structures could not avoid manual handling such as directly gluing the top and bottom layers of the structure, or transferring pre-strained patterns on the substrate, which has limited the production efficiency at a very low level.
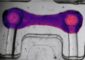
However, Professor Kim's team created 3D flexible structures by generating covalent bonds only at the edges of patterns formed between two polymeric thin films with plasma and by injecting air into non-bonded patterns (namely, balloons) to inflate them. Moreover, the new 3D structures can be used as a sensor or actuator1 because metal wires can be easily patterned inside and outside the balloons.
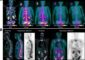
A customized 3D device that is in contact with a complicated surface can also be produced using the technology developed by Professor Kim's team. Since the 3D device is inflated like a balloon where the device is put on, it can have a customized shape along the curvature of a body part with a complex surface, like the human brain.
In addition, wire patterns in the micrometer scale can be easily formed inside and outside the 3D structure, which has been difficult so far in the production of 3D structures using conventional microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) technologies. It is expected to be widely applied, for instance, for pressure measurement inside the body including the cranium, devices with electrical stimulation and detection functions, and soft robots.
###
The result of this study was published on the supplementary front page of the ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces of the American Chemical Society on Wednesday, October 2. This study was conducted with supports from Basic Research Program of the South Korean Ministry of Science and ICT as well as the DGIST. Ph.D. candidate Hyunmin Moon in the Department of Robotics Engineering and post-doctoral researcher Namsun Chou at Korea Institute of Science and Technology participated in the research as the first co-authors.
1 Actuator: A device that operates a machine using electric power.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…