Using organisms to decontaminate soil
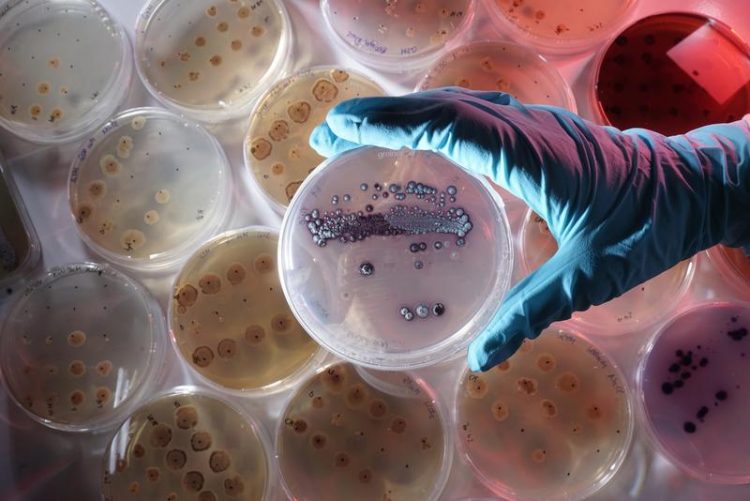
Researchers from University of Jena are looking for bacteria - in the picture: Petri dish with the bacterium Streptomyces lividans - that fix heavy metals dissolved in the soil as biominerals. Image: Jan-Peter Kasper/FSU
Decontaminating the legacy of uranium mining in the GDR
“Even today, 30 years after its end, the GDR is still ranked the third largest producer of uranium in the world. In eastern Thuringia and western Saxony, for example, more than 210,000 tonnes of the radioactive element were mined,” says the microbiologist Prof. Erika Kothe of the University of Jena. She is leading the project together with the geoscientist Prof. Thorsten Schäfer.
Following the uranium mining of the past, in the project, a possible re-use of the former mining areas is to be tested. Essentially, the soils there are still contaminated with heavy metals; acids are formed which dissolve the toxic metals and can thus pose a hazard to the groundwater.
In the former mining area near Ronneburg, which is nowadays managed by the government-owned Wismut GmbH, four test sites will be examined within the project. During the past four years, the University’s geoscientists and microbiologists have been examining biocompatible methods for a long-term land use there, in particular for biomass production.
Based on the successes of the first funding phase, the government-funded project USER2 is about to focus on implementation of heavy metal land farming for sustainable landscape design and production of renewable energies from radionuclide-contaminated areas.
For example, the research teams had planted trees, which appeared to grow in spite of the pollution, and may serve as renewable energy. Mycorrhiza, e.g. fly agarics of bay boletes, supply the trees with water and nutrient salts. In turn, the trees supply the fungi with products from photosynthesis.
“Our goal is to find the best combination of fungi and trees,” says Erika Kothe. “The heavy metals should remain in the mushrooms or – better still – soil bacteria should convert them into biominerals.” To remove the toxins from the soils, the teams use an undergrowth.
Bioremediation of soil and re-use
To remove the metals from the soil, the team plants herbaceous plants such as red fescue or rye. “The herbaceous plants remove the toxins from the soil. They can then be harvested, incinerated, and the ashes safely deposited,” explains Kothe.
“This way, the soil is improved in the long-term without major technical effort. Moreover, the trees planted can be burnt or their lignocellulose can be chemically converted into biofuel.” In addition, the herbaceous undergrowth protects the soil against erosion. Like the trees, the undergrowth, too, can benefit from soil bacteria and fungi provided that suitable microbes can be found.
During this new 3-year-long project, the interdisciplinary team wants to continue with the various trial plantings on site, curb soil erosion, and take stock. Apart from these, they will study the transport of heavy metals in the form of nanoparticles in water. An integral part of the project are students who conduct annual intensive measurements and analyses of the plants, fungi, and soil bacteria.
This one-week visit to the site in the fifth semester is part of the bachelor's programme in biogeosciences at the University of Jena. Yet students are introduced to the test site even at an earlier stage. Each year there is an excursion to Ronneburg being part of the lecture on bio-geo interactions during their first semester.
Studying biogeosciences at the Friedrich Schiller University Jena
Anyone interested in this topic can study biogeosciences at the University in Jena. If you want to apply for the bachelor’s programme in biogeosciences (https://www.uni-jena.de/Studium/Studienangebot/BSc_Biogeowissenschaften.html), you should do so by 15 September 2019. The University also offers a master’s programme (https://www.uni-jena.de/en/Studies/Study+programme/MSc_Biogeosciences.html) on the same subject.
Prof. Dr Erika Kothe
Institute of Microbiology of Friedrich Schiller University Jena
Neugasse 25
07743 Jena, Germany
Phone: +49 (0)3641 / 949291
Email: erika.kothe[at]uni-jena.de
Prof. Dr Thorsten Schäfer
Institute of Geosciences of Friedrich Schiller University Jena
Burgweg 11
07749 Jena, Germany
Phone: +49 (0)3641 / 948640
Email: thorsten.schaefer[at]uni-jena.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















