Untangling a protein’s influences
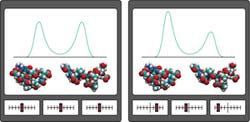
Figure 1: DIPA reveals shifts in protein conformation that arise from the strengthening or weakening effects of perturbing protein–water interactions. The bars along the bottom indicate the relative strength of the perturbations (weak, left; strong, right). <br>Copyright : 2011 Yohei M. Koyama<br>
Most proteins have multiple moving parts that rearrange into different conformations to execute particular functions. Such changes may be induced by molecules in the immediate environment, including water and similar solvents as well as other molecules or drugs that a protein might encounter.
A new computational approach devised by Yohei Koyama and Hiroki Ueda at the RIKEN Quantitative Biology Center, Kobe, and Tetsuya Kobayashi of the University of Tokyo now provides researchers with the means to understand how specific interactions between environmental molecules and a given protein facilitate particular conformational rearrangements1.
In the past, researchers have focused on the movement of specific atomic coordinates, using a statistical tool called principal component analysis (PCA) to identify segments of the protein that collectively contribute to a given rearrangement. However, such approaches simply map a protein’s movements rather than clarifying interactions that contribute to those changes. To address this limitation, Koyama, Ueda and Kobayashi developed a method called distance-dependent intermolecular perturbation analysis (DIPA), which uses PCA to characterize how subsets of environmental molecules contribute to conformational shifts.
“Perturbation analysis is a method to understand complex systems by observing responses to changes in the system,” explains Koyama. “For example, to understand the function of a machine without a manual, we sometimes manipulate the controls and observe its response.” Accordingly, DIPA simulates the manipulation of different environmental molecules and determines whether they favor particular conformational states for a protein (Fig. 1).
The researchers initially used DIPA to simulate the influence of surrounding water on a chemically capped version of the amino acid alanine and identified three conformational states. In a subsequent analysis, they used a larger molecule called chignolin, a hairpin-shaped polypeptide containing ten amino acids, and observed four states and the environmental influences that stabilize those states. “We observed that molecular states can be identified clearly in terms of intermolecular protein–water interactions,” says Koyama.
DIPA is a powerful tool, but the researchers cannot yet apply it to the movements of full-sized proteins, as existing computational hardware is inadequate for such demanding molecular dynamics simulations. “Current simulations are performed over timescales of a few microseconds,” says Koyama, “but many proteins manifest their functions over an order of many microseconds or even milliseconds.” However, supercomputing initiatives underway at RIKEN—such as the ultra-fast ‘K computer’ slated for completion in 2012—could help bring these capabilities within reach, at which point DIPA promises to become a potent resource for the rational design of protein-specific drugs.
The corresponding author for this highlight is based at the Laboratory for Synthetic Biology, RIKEN Quantitative Biology Center
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















