UCI researchers create retina from human embryonic stem cells

UC Irvine scientists have created an eight-layer, early stage retina from human embryonic stem cells, the first three-dimensional tissue structure to be made from stem cells.
It also marks the first step toward the development of transplant-ready retinas to treat eye disorders such as retinitis pigmentosa and macular degeneration that affect millions.
“We made a complex structure consisting of many cell types,” said study leader Hans Keirstead of the Reeve-Irvine Research Center and the Sue and Bill Gross Stem Cell Research Center at UCI. “This is a major advance in our quest to treat retinal disease.”
In previous studies on spinal cord injury, the Keirstead group originated a method by which human embryonic stem cells could be directed to become specific cell types, a process called differentiation. Results of those studies are leading to the world’s first clinical trial using a stem cell-based therapy for acute spinal cord injury.
In this study, the Keirstead team utilized the differentiation technique to create the multiple cell types necessary for the retina. The greatest challenge, Keirstead said, was in the engineering. To mimic early stage retinal development, the researchers needed to build microscopic gradients for solutions in which to bathe the stem cells to initiate specific differentiation paths.
“Creating this complex tissue is a first for the stem cell field,” Keirstead said. “Dr. Gabriel Nistor in our group addressed a really interesting scientific problem with an engineering solution, showing that gradients of solutions can create complex stem cell-based tissues.”
The retina is the inside back layer of the eye that records the images a person sees and sends them via the optic nerve from the eye to the brain. Retinal diseases are particularly damaging to sight. More than 10 million Americans suffer from macular degeneration, the leading cause of blindness in people over 55. About 100,000 have retinitis pigmentosa, a progressive, genetic disorder that usually manifests in childhood.
“What’s so exciting with our discovery,” Keirstead said, “is that creating transplantable retinas from stem cells could help millions of people, and we are well on the way.”
The UCI researchers are testing the early-stage retinas in animal models to learn how much they improve vision. Positive results would lead to human clinical trials.
The study appears online in the Journal of Neuroscience Methods. Nistor, Magdalene J. Seiler, Fengrong Yan and David Ferguson contributed to the effort, supported by The Lincy Foundation and private donations to the Keirstead group.
About the University of California, Irvine: Founded in 1965, UCI is a top-ranked university dedicated to research, scholarship and community service. Led by Chancellor Michael Drake since 2005, UCI is among the most dynamic campuses in the University of California system, with nearly 28,000 undergraduate and graduate students, 1,100 faculty and 9,000 staff. Orange County’s largest employer, UCI contributes an annual economic impact of $3.9 billion. For more UCI news, visit www.today.uci.edu.
News Radio: UCI maintains on campus an ISDN line for conducting interviews with its faculty and experts. Use of this line is available for a fee to radio news programs/stations that wish to interview UCI faculty and experts. Use of the ISDN line is subject to availability and approval by the university.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uci.eduAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
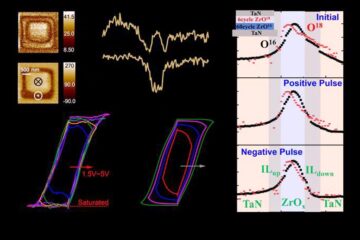
Evidence for reversible oxygen ion movement during electrical pulsing
…enabler of the emerging ferroelectricity in binary oxides. In a recent study published in Materials Futures, researchers have uncovered a pivotal mechanism driving the emergence of ferroelectricity in binary oxides….
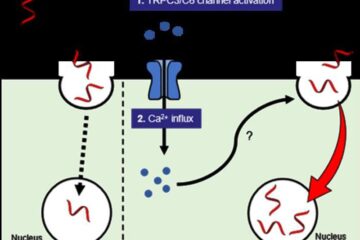
Next-generation treatments hitch a ride into cancer cells
Researchers from Osaka University discover that opening a channel into cancer cells helps antisense oligonucleotide drugs reach their targets. Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) are next-generation drugs that can treat disease by…

Boron deficiency: oilseed rape reacts as with infection and pest infestation
Genetic mechanisms uncovered… Boron deficiency has a devastating effect on oilseed rape and related plants. However, little is known about the underlying genetic mechanisms. A study shows that the response…





















