Traffic Cops of the Immune System
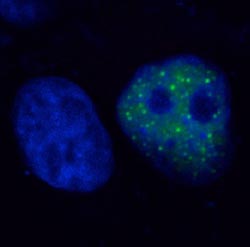
The figure shows the localization of IkBNS in the cell. IkBNS molecules (green) occur in dotted structures within the cell nucleus (blue). The function of these structures is, however, largely unknown.<br><br>HZI / Schmitz<br>
A certain type of immune cell – the regulatory T cell, or Treg for short – is in charge of putting on the brakes on the immune response. In a way, this cell type might be considered the immune system’s traffic cop.
Now, scientists at the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research (HZI) have looked into the origin of Tregs and uncovered a central role played by the protein IκBNS. Armed with this knowledge, the researchers hope to manipulate Tregs in order to either inhibit or activate the immune system. Biochemist Prof. Ingo Schmitz and his team have now published their findings in the scientific journal Immunity.
The immune system is a complex network of different types of cells and chemical messengers. The regulatory cells and other immune cells exist together in a delicate balance. Any disturbance of this balance could have serious consequences: If there are too many Tregs, the immune system might be “thwarted” and little would stand in the way of infections or tumors spreading throughout the body. By contrast, if there are too few Tregs, other immune cells could get out of control and attack the body's own tissues: autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or the chronic inflammatory bowel disease ulcerative colitis may be a consequence. Tregs also play an important role following an organ transplant as they decide whether the body will accept or reject the donor organ.
But what it is exactly that makes immature immune cells choose the “police officer career” had eluded scientists. Schmitz and his team from the HZI, the Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg, the Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin, the Harvard Medical School Boston, the TWINCORE in Hanover, the Eberhard Karls University Tübingen and the Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf were now able to demonstrate that the transcription factor IκBNS contributes considerably to Treg development. The molecule promotes formation of the protein Foxp3, the Tregs' central feature. IκBNS influences the large NFκB family of transcription factors. These signaling molecules trigger a number of different inflammatory responses elicited by the immune system. “It was therefore all the more surprising for us when we identified IκBNS’ central role in Treg maturation.
Essentially, these are cells capable of constraining inflammation – even though IκBNS in no way influences the function of regulatory T cells,” explains Dr. Marc Schuster, one of Schmitz' colleagues at HZI and the article’s first author. The researchers tested their hypothesis regarding IκBNS’ central role in Treg development in mice that are missing this factor. Since cells that lack IκBNS do not “become cops,” the immune system's effector cells are undamped and could trigger chronic inflammation of the intestine.
The results have confirmed that further research on IκBNS is of interest from a medical perspective as well. On the one hand, it allows predicting diseases: If IκBNS is fraught with errors, this could trigger autoimmune disorders. On the other hand, one potential therapeutic goal might be “to manipulate IκBNS in such a way that we can control the number of Tregs,” explains Schmitz, who, in addition to his HZI research, also has a chair at the Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg. “IκBNS stabilization could benefit autoimmune disease therapy. As far as infections or tumors are concerned, we would need to inhibit IκBNS to decrease the number of regulatory T cells. Of course, all that is still in the very distant future.” But because IκBNS also plays an important role in effector cell activation, an intervention might have unforeseen consequences. “This is a challenge you face with many different therapeutic targets,” adds Schmitz.
Original publication:
Marc Schuster, Rainer Glauben, Carlos Plaza-Sirvent, Lisa Schreiber, Michaela Annemann, Stefan Floess, Anja A. Kühl, Linda K. Clayton, Tim Sparwasser, Klaus Schulze-Osthoff, Klaus Pfeffer, Jochen Huehn, Britta Siegmund, Ingo Schmitz
The atypical NFκB inhibitor IκBNS mediates regulatory T cell development by regulating Foxp3 induction
Immunity, 2012
The research group “Systems-oriented Immunology and Inflammation Research” explores the molecular processes that make immune cells tolerant to the body’s own tissues. This includes especially the cellular suicide program apoptosis.
The Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research
At the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research in Braunschweig, scientists are studying microbial virulence factors, host-pathogen interactions and immunity. The goal is to develop strategies for the diagnosis, prevention and therapy of human infectious diseases.
The Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg:
One of the Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg Medical Faculty’s research emphases is “Immunology including molecular medicine relating to inflammation”. The goal is to develop new therapeutic approaches and deliver them to the patient.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…





















