Textile Solar Cells
Textile solar cells are an ideal power source for small electronic devices incorporated into clothing. In the journal Angewandte Chemie,Chinese scientists have now introduced novel solar cells in the form of fibers that can be woven into a textile. The flexible, coaxial cells are based on a perovskite material and carbon nanotubes; they stand out due to their excellent energy conversion efficiency of 3.3 % and their low production cost.
The dilemma for solar cells: they are either inexpensive and inefficient, or they have a reasonable efficiency and are very expensive. One solution may come from solar cells made of perovskite materials, which are less expensive than silicon and do not require any expensive additives. Perovskites are materials with a special crystal structure that is like that of perovskite, a calcium titanate.
These structures are often semiconductors and absorb light relatively efficiently. Most importantly, they can move electrons excited by light for long distances within the crystal lattice before they return to their energetic ground state and take up a solid position – a property that is very important in solar cells.
A team led by Hisheng Peng at Fudan University in Shanghai has now developed perovskite solar cells in the form of flexible fibers that can be woven into electronic textiles. Their production process is relatively simple and inexpensive because it uses a solution-based process to build up the layers.
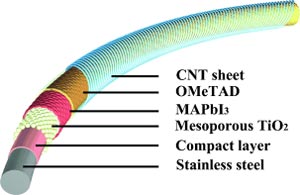
The anode is a fine stainless steel wire coated with a compact n-semiconducting titanium dioxide layer. A layer of porous nanocrystalline titanium dioxide is deposited on top of this. This provides a large surface area for the subsequent deposition of the perovskite material CH3NH3PbI3.
This is followed by a layer made of a special organic material. Finally a transparent layer of aligned carbon nanotubes is continuously wound over the whole thing to act as the cathode. The resulting fiber is so fine and flexible that it can be woven into textiles.
The perovskite layer absorbs light, that excites electrons and sets them free, causing a charge separation between the electrons and the formally positively charged “holes” The electrons enter the conducting band of the compact titanium dioxide layer and move to the anode.
The “holes” are captured by the organic layer. The large surface area and the high electrical conductivity of the carbon nanotube cathode aid in the rapid conduction of the charges with high photoelectric currents. The fiber solar cell can attain an energy conversion efficiency of 3.3 %, exceeding that of all previous coaxial fiber solar cells made with either dyes or polymers.
About the Author
Dr. Huisheng Peng is a Professor of Department of Macromolecular Science and Laboratory of Advanced Materials at Fudan University. His research centers on functional composite materials and their energy applications. He and co-workers created aligned carbon nanotube/polymer composites and developed novel fiber-shaped solar cells, Li-ion batteries and electrochemical supercapacitors.
Author: Huisheng Peng, Fudan University, Shanghai (China), http://www.polymer.fudan.edu.cn/polymer/research/Penghs/main_en.htm
Title: Integrating Perovskite Solar Cells into a Flexible Fiber
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, Permalink to the article: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201404973
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















