Synapses – stability in transformation
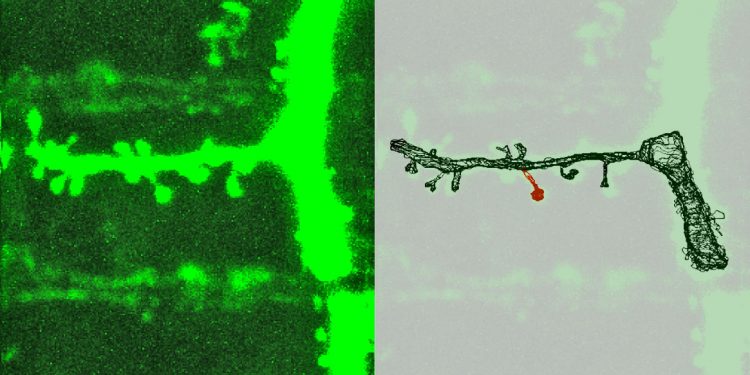
During the learning processes, extensions grow on neurons. Synapses are located at the end of these extensions (left: as seen in nature; right: reconstruction). When the synapse growth is based on the correlated development of all synaptic components, it can remain stable for long periods of time. © MPI of Neurobiology/ Meyer
Synapses are the points of contact at which information is transmitted between neurons. Without them, we would not be able to form thoughts or remember things. For memories to endure, synapses sometimes have to remain stable for very long periods.
But how can a synapse last if its components have to be replaced regularly? Scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology in Martinsried near Munich have taken a decisive step towards answering this question. They have succeeded in demonstrating that when a synapse is formed, all of the components must grow in a coordinated way.
This is the only way that a long-term functioning synapse, –the basic prerequisite of learning and memory processes, can be formed. This kind of interactive system must allow for the replacement of individual molecules while the other components stabilise the synapse.
Nothing lasts forever. This principle also applies to the proteins that make up the points of contact between our neurons. It is due to these proteins that the information arriving at a synapse can be transmitted and then received by the next neuron. When we learn something, new synapses are created or existing ones are strengthened. To enable us to retain long-term memories, synapses must remain stable for long periods of time, up to an entire lifetime. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology in Martinsried near Munich have found an explanation as to how a synapse achieves remaining stable for a long time despite the fact that its proteins must be renewed regularly.
“We were interested first of all in what happens to the different components of a synapse when it grows during a learning process,” explains study leader Volker Scheuss. An understanding of how the components grow could also provide information about the long-term stability of synapses. Hence, the researchers studied the growth of synapses in tissue culture dishes following exposure to a (learning) stimulus. To do this, they deliberately activated individual synapses using the neurotransmitter glutamate: scientists have long known that glutamate plays an important role in learning processes and stimulates the growth of synapses. Over the following hours, the researchers observed the stimulated synapses and control synapses under a 2-photon microscope. To confirm the observed effects, they then examined individual synapses with the help of an electron microscope. “When you consider that individual synapses are only around one thousandth of a millimetre in size, this was quite a Sisyphean task,” says Tobias Bonhoeffer, the Director of the department where the research was carried out.
The scientists discovered that during synapse growth the different protein structures always grew coordinated with each other. If one structural component was enlarged alone, or in a way that was not correctly correlated with the other components, its structural change would collapse soon after. Synapses with such incomplete changes cannot store any long-term memories.
The study findings show that the order and interaction between synaptic components is finely tuned and correlated. “In a system of this kind, it should be entirely possible to replace individual proteins while the rest of the structure maintains its integrity,” says Scheuss. However, if an entire group of components breaks away, the synapse is destabilised. This is also an important process given that the brain could not function correctly without the capacity to forget things. Hence, the study’s results provide not only important insight into the functioning and structure of synapses, they also establish a basis for a better understanding of memory loss, for example in the case of degenerative brain diseases.
Contact
Dr. Stefanie Merker
Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology, Martinsried
Phone: +49 89 8578-3514
Prof. Dr. Tobias Bonhoeffer
Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology, Martinsried
Phone: +49 89 8578-3751
Fax: +49 89 8578-2481
Email:tobias.bonhoeffer@neuro.mpg.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Combatting disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communication
In a significant milestone for quantum communication technology, an experiment has demonstrated how networks can be leveraged to combat disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communications. The international effort led by researchers…

Stretchable quantum dot display
Intrinsically stretchable quantum dot-based light-emitting diodes achieved record-breaking performance. A team of South Korean scientists led by Professor KIM Dae-Hyeong of the Center for Nanoparticle Research within the Institute for…

Internet can achieve quantum speed with light saved as sound
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen’s Niels Bohr Institute have developed a new way to create quantum memory: A small drum can store data sent with light in its sonic…





















