Study reveals how bacteria build essential carbon-fixing machinery
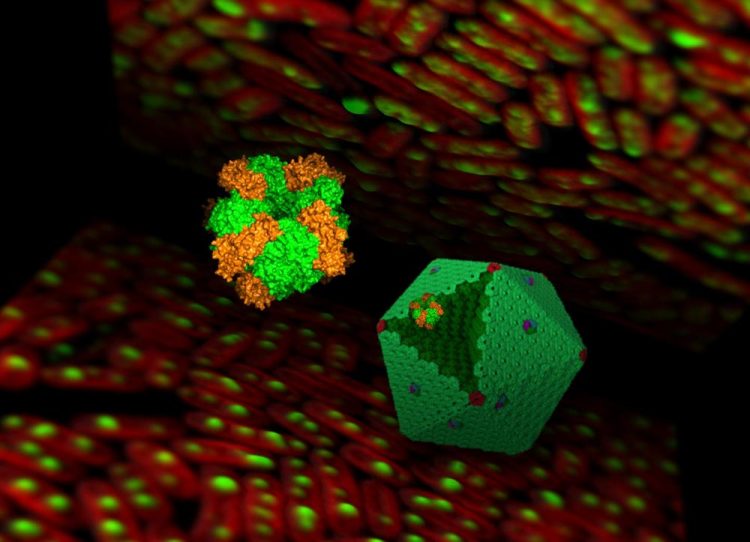
Illustration of a complex carboxysome structure and Rubisco enzymes Credit: Luning Liu
Cyanobacteria are an ancient group of photosynthetic microbes that occur in the ocean and most inland waters. They have evolved a protein organelle, called the carboxysome, to convert environmental carbon dioxide into sugar in an efficient way.
A key step of this conversion is catalysed by a carbon-fixing enzyme Rubisco. However, Rubisco is poorly 'designed' because it is inefficient in fixing CO2 when a high level of O2 is around.
Cyanobacterial carboxysomes sequester and concentrate Rubisco enzymes within the separated compartment and provide a low O2 environment for Rubisco to improve carbon fixation.
“It is a mystery how cyanobacterial cells generate the complex carboxysome structure and pack Rubisco enzymes in the organelle to have biological functions,” said Luning Liu, a Professor at the University of Liverpool, and a senior author on this paper. “My research group has interest in addressing the key questions in this biological process.”
The formation of the Rubisco complex involves a few 'helping' proteins called chaperones, including a protein named Rubisco assembly factor 1 (Raf1).
To understand the exact roles of Raf1, the team used state-of-the-art microscopies, such as confocal fluorescence microscopy, electron microscopy, and cryo-electron microscopy, combined with molecular biology and biochemical techniques, to study how Raf1 interacts with Rubisco subunits to promote the assembly of Rubisco, and how carboxysome formation is affected when cells do not produce Raf1.
The researchers proved that Raf1 is vital for building the Rubisco complex. Without Raf1, the Rubisco complexes are less efficiently assembled and cannot be densely packed inside the carboxysomes. This could greatly affect the construction of carboxysomes and therefor the growth of cyanobacterial cells.
“This is the first time that we have determined the function of Rubisco assembly chaperones in the biosynthesis of carboxysomes in cyanobacterial cells,” said Dr Fang Huang, a Leverhulme Trust Early Career Fellow, and the first author on this paper.
“We are very excited about this finding. It also allowed us to propose a new working model of carboxysome biogenesis, which teach us in detail how Rubisco complexes are generated, how Raf1 drive Rubisco packing, and how the entire carboxysome structure is constructed.”
Currently, there is a tremendous interest in transferring carboxysomes into crop plants to improve crop yields and food production. This study may provide important information required for producing intact and functional carbon-fixing machinery.
###
The project was funded by Royal Society, Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC), and Leverhulme Trust. The project was carried out in collaboration with the Centre for Cell Imaging and Biomedical Electron Microscopy Unit at the University of Liverpool.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















