Stem cell divisions in the adult brain seen for the first time
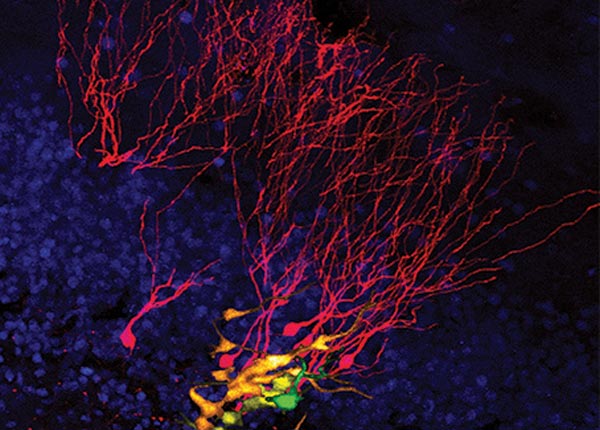
An individual neural stem cell (green) and its daughter neurons (depending on the age shown in yellow, orange and red) that were generated over 2 months . UZH
The generation of new nerve cells was once thought to taper off at the end of embryonic development. However, recent research has shown that the adult brain can generate new nerve cells throughout life. One of the areas where this happens is the hippocampus, a brain structure that determines many types of learning and memory, deciding what is remembered and what is forgotten.
A window into the brain
In a new study published in Science, the laboratory of Sebastian Jessberger, professor in the Brain Research Institute of the University of Zurich, has shown for the first time the process by which neural stem cells divide and newborn neurons integrate in the adult mouse hippocampus.
The study, which was led by postdoc Gregor Pilz and PhD student Sara Bottes, used in vivo 2-photon imaging and genetic labeling of neural stem cells in order to observe stem cell divisions as they happened, and to follow the maturation of new nerve cells for up to two months.
By observing the cells in action and over time the team showed how most stem cells divide only for a few rounds before they mature into neurons. These results offer an explanation as to why the number of newborn cells dramatically declines with advancing age.
“In the past it was deemed technically impossible to follow single cell stem cells in the brain over time given the deep localization of the hippocampus in the brain”, said Jessberger. He added that the breakthrough was only made possible by forming an interdisciplinary team.
“We were fortunate that a group of collaborators, including Fritjof Helmchen from the Brain Research Institute and David Jörg and Benjamin Simons from the University of Cambridge, joined efforts to bring together their expertise in deep brain imaging and theoretical modeling, which allowed us to ob-tain and understand our data”.
Stem cells as therapeutic targets for brain diseases
The study answered longstanding questions in the field, but the researchers stated that this is just the beginning of many more experiments aimed at understanding how our brains are able to form new nerve cells throughout life. “In the future, we hope that we will be able to use neural stem cells for brain repair – for example for diseases such as cognitive aging, Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease or major depression”, summarizes Jessberger.
Other researchers involved were Marion Betizeau and Stefano Carta from the Brain Research Institute, UZH.
Literature:
Gregor-Alexander Pilz, Sara Bottes, Marion Betizeau, David J. Jörg, Stefano Carta, Benjamin D. Simons, Fritjof Helmchen, Sebastian Jessberger. Live imaging of neurogenesis in the adult mouse hippocampus. Science. 9 February 2018. DOI: 10.1126/science.aao5056.
Project funding
The study was supported by the European Research Council, Swiss National Science Founda-tion, Dr. Eric Slack-Gyr foundation, the European Molecular Biology Organization, the Wellcome Trust, and the Neuroscience Zurich Center.
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Sebastian Jessberger
Brain Research Institute
Universität Zürich
Tel. +41 44 635 33 70
E-Mail: jessberger@hifo.uzh
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…





















