Small change for a big improvement – halogen bonds and drug discovery
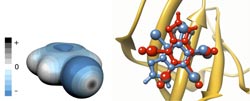
Left panel: the charge distribution around the bromobenzene molecule. The regions of negative electrostatic potential are in blue, positive regions in grey. The grey disc in the forefront represents the ?-hole. Right panel: the overlay of the predicted binding poses of K17 inhibitor of casein kinase 2 (PDB code 2OXY) with (red) and without (blue) explicit sigma-holes (ESH) and comparison with the crystal structure (grey).<br>Image: Agnieszka Bronowska / HITS<br>
Halogen chemistry has been exploited by medicinal chemists for nearly 70 years. To date, halogens were regarded useful for optimization of so-called ADMET properties (the acronym stands for absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, toxicity) – they improve oral absorption and facilitate crossing biological barriers by prospective drugs, they are useful for filling small hydrophobic cavities present in many protein targets, and they prolong lifetime of the drug.
In short: They make compounds of interest more drug-like. However, direct interactions mediated by halogen atoms have been much ignored in pre-clinical drug development.
Recently, scientists from Heidelberg and Prague, working in quantum chemistry and structure-based drug design, have developed a new tool for the usage of halogen bonds for computational medicinal chemistry and drug discovery applications. The study, led by Dr. Agnieszka Bronowska from the Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies (HITS) and conducted in cooperation with scientists from the Czech Academy of Sciences, has been published in Chemical Communication.
Most halogens – except fluorine – have unique properties which allow them to stabilize direct interaction between prospective drugs and their protein targets. These properties are of quantum-chemical origin; namely, the anisotropy of charge distribution around the halogen atom, when it is bound to an electron-withdrawing substrate. Unexpectedly, despite of being negatively charged, halogens have regions which remain positively charged (Figure 1, left panel). These regions, called sigma-holes, are responsible for the directional and stabilizing character of halogen bonding with other electronegative atoms, such as oxygen or nitrogen.
Overlooking sigma-holes leads to errors in predictions of structure and energetics of drug-protein complexes and thus to failure in drug development.
By approximating the positively charged sigma-hole with a massless, charged pseudo-atom (denoted as explicit sigma-hole or ESH), Agnieszka Bronowska and her colleagues incorporated a quantum-chemical effect into faster (and much less accurate) computational methods applicable to structure-based drug design. “We tested nearly a hundred complexes between medicinally relevant proteins and halogenated molecules”, Bronowska says. “The results showed significant improvement in the description of such complexes upon introduction of ESH.”
The new method is already used by research groups in the Czech Republic, in the United Kingdom and in the U.S. for designing novel compounds to treat chemotherapy-resistant cancers, infectious diseases, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Scientific Publication:
Plugging the explicit sigma-holes in molecular docking. Michal Kolár, Pavel Hobza and Agnieszka K. Bronowska. Chem. Commun., 2013,49 (10), 981-983
DOI: 10.1039/C2CC37584B
http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2013/cc/c2cc37584b
Scientific Contact:
Dr. Agnieszka Bronowska
Molecular Biomechanics Group (MBM)
Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies (HITS)
Agnieszka.bronowska@h-its.org
Press Contact:
Dr. Peter Saueressig
Public Relations
Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies (HITS)
Phone: +49-6221-533245
Peter.saueressig@h-its.org
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















